Definition of Molecular Geometry
Miscellanea / / January 11, 2022
Conceptual definition
It is the structure of a molecule that determines the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make it up in space.

Chemical engineer
Molecular geometries are currently defined based on the Theory of Repulsion of Electronic Pairs of the Valencia Layer (TRPECV). This theory allows predicting the behavior chemical of substances (specifically covalent) and helps to understand the distribution electronics, leading to geometry of the molecule. This, in turn, allows us to understand many of the properties that substances acquire.
This Theory is based on a series of fundamental pillars that we will review and then try to understand their application practice. In the first place, bonded and unbonded (valence) electrons are thought of as a sea of electrons that, by possess the same type of charge, they repel each other, so they will always be located as far away from the central atom of the molecule.
Second, this "sea" of electrons or "electronic cloud" forms areas of high electron densities, that are constituted in bonds, where the electrons are shared or in pairs of electrons not shared. In turn, the bonds that are formed can be single, double or even triple.
Finally, for decide molecular geometry, it is very helpful to have the Lewis structure, where the amount of electron densities around the central atom will be counted and this will give indication from the name of its geometry and the shape that the molecule takes three-dimensionally.
It should be noted that these densities will be located as far apart as possible, in order to adopt the most stable structure and where there is less repulsion. This is how, first the electronic geometry is identified and then the molecular geometry.
Six levels of density
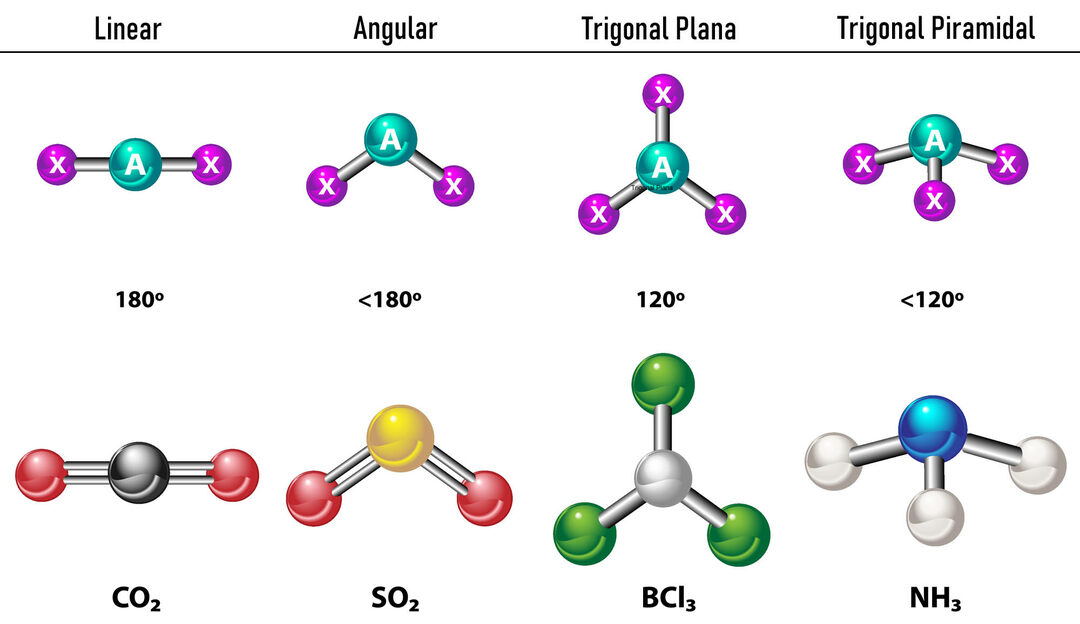
In the case that there are two electron densities around the central atom, the bonds will be located as far apart between them, that is to say 180º from each other and, therefore, their electronic geometry is linear and molecularly it is also linear.
In the case that there are three electron densities around the central atom, there are two options: three bonds or two bonds and one unbound pair. If there are three bonds, the electronic geometry is Trigonal Flat, with 120º angles between bonds and molecular geometry takes the same name. Now, if there is a non-bonded pair, they repel each other with more intensity that bonded charges therefore tend to compress bond angles. The angle between the free pair and each bond is 120º and the electronic geometry is Trigonal Plane while the molecular geometry is Angular.
In the case that there are four electron densities around the central atom, the electronic geometry is tetrahedral. If all four pairs of electrons are bonded, their molecular geometry coincides in name with their electronic geometry and the bond angle is 109.5º. Now, if one of the pairs is free, the bond angle gets smaller (107º) and the molecular geometry is type Trigonal Pyramid. Finally, if two are free pairs and two are bonded, the bond angle is 104.5º while the molecular geometry is called Angular.
When the electron densities around the central atom amount to five, it is called a Trigonal Bipyramid its electronic geometry. If all the charges are linked, there are angles of 120ºC between the equatorially located links and 90º between the axial with the equiatorial ones. Now, molecular geometry is also called Trigonal Bipyramid while, having four linked pairs and one free pair, the molecular geometry is distorted forming the well-known "rocker”, There the name it acquires is Distorted tetrahedron. Whereas, if two of the five pairs of electrons are free and three of them are bonded, it has a “T” -shaped geometry and its name is precisely due to its structure. Finally, if it is the reverse, three free pairs and two bonded charges, the molecular geometry is linear.
Finally, there are six electron densities around the central atom and an octahedron is formed, hence its name in electronic geometry. Similarly, the molecular geometry is named if all its pairs are linked. If you have five linked pairs and one free pair, the molecular geometry is Square Base Pyramid. If you have four bonded pairs and two free pairs, the molecular geometry is Square Flat.
Figure: Sweet Nature
Topics in Molecular Geometry