Definition of Modern Physics
Inhibition String Theory / / April 02, 2023

Industrial Engineer, MSc in Physics, and EdD
Modern Physics is a field of study that has developed since the 20th century, ranging from quantum physics to relativity. In general, two fundamental categories for understanding the behavior of objects at different scales, whether they are elementary particles or galaxies. whole. Likewise, Modern Physics is responsible for the study and discovery of new particles. subatomic, as well as its relationship with other scientific fields such as molecular biology and modern technologies.
The importance of Modern Physics lies in its ability to explain many natural phenomena that were previously indecipherable through classical Physics. For example, Quantum Mechanics, along with generalized relativity, have made it possible to explain quantum effects, the contraction of space, the dilation of time or the effects that are generated at speeds close to that of light. Likewise, the main difference between Classical Theoretical Physics and Modern Physics is that the latter establishes a more complex in the models or interpretations, and has a greater capacity for experimentation predictions considering a greater variety of conditions.
With the emergence of quantum physics, great technological advances have been developed, for example, in the field of electronics from the transistor and other components.
Currently, there are numerous studies on the fundamental properties that govern some of the most complex aspects of Physics. Modern, being necessary to have innovative equipment and advanced technologies (such as accelerators of particles). The results obtained can be used to create more efficient devices that improve the quality of life, as well as a better understanding of the universe.
It supposes a field of study that covers from the end of the 19th century to the present day, and is related to the research and understanding of the fundamental laws of the physical world, as well as their practical application in technology modern. For this reason, it has become key to understanding the basic principles behind many recent scientific advances, including nuclear power, digital computers, and nanotechnology.
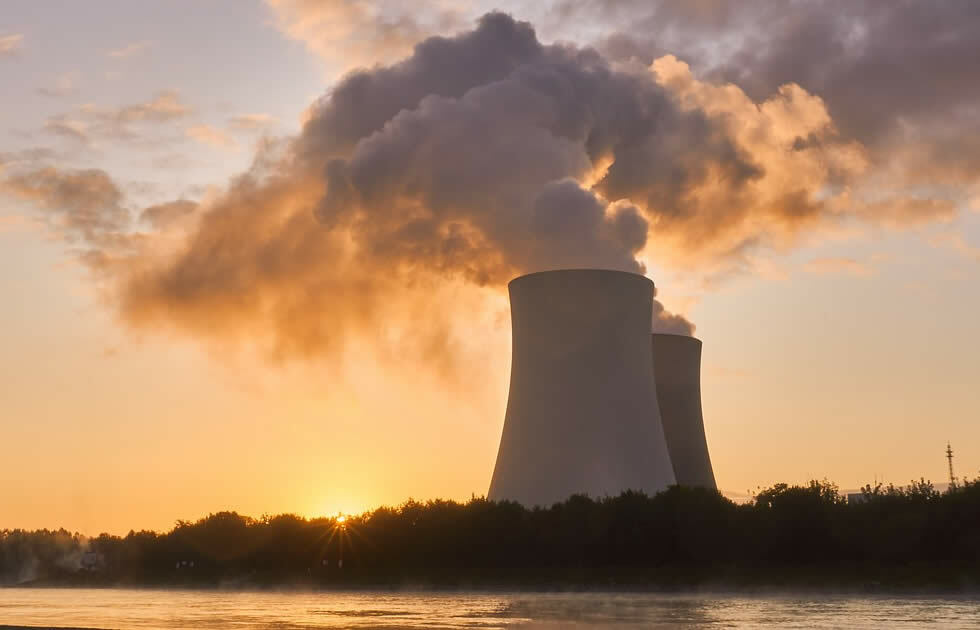

The production of electricity from nuclear sources has been possible due to the contributions of Modern Physics in the energy field.
There are numerous technological fields particularly related to Modern Physics that have been developed as studies continue and the available technology improves. Thus, among the areas of science that have benefited, it is possible to highlight materials and mechanical engineering, biomechanics, computing, processes in medicinal laboratories, transportation and construction systems, among others.
Theory of relativity
The work carried out by Albert Einstein in 1905 marks the formal beginning of the scientific advance towards what we currently know as «Modern Physics». Their conceptual depths allowed researchers to visualize complex processes such as nuclear energy, gravitational waves and even black holes within the global context of cosmology modern.

Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955), is considered one of the most outstanding scientists of Modern Physics.
The theory of relativity is a set of concepts, equations and scientific foundations proposed by Einstein in his search to respond to the mathematical incompatibility between classical physics in the area of Newtonian mechanics and the electromagnetism. These foundations are developed in two theories:
Special or restricted relativity: it was proposed in 1905 and explains the movement of bodies without the presence of gravitational forces in a flat time and space system in frames of references inertial. It allowed consolidating Newtonian mechanics with Maxwell's electromagnetic theory.
General relativity: it was postulated in 1915 and deals with the concepts of reference systems and gravity. It is said to be general, because it extends the principle of special relativity and states that the geometry of space - time is modified by the presence of matter.
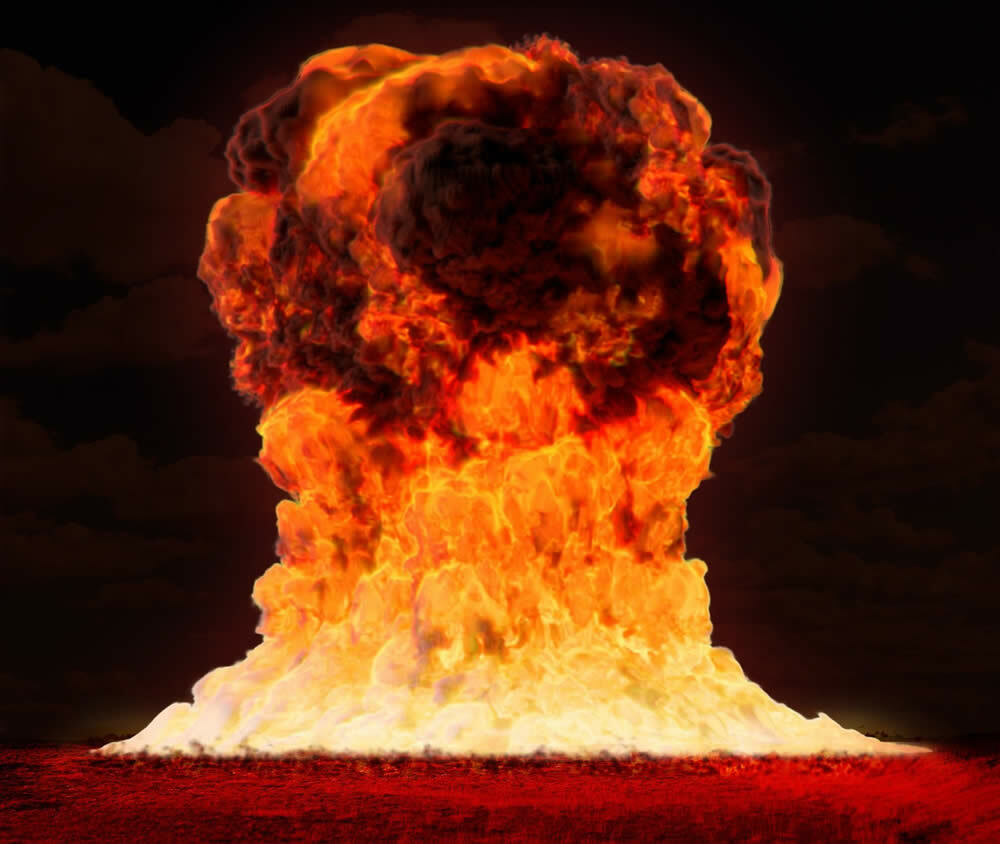

Unfortunately, not all the findings of Modern Physics have been applied to technologies and advances for the benefit of humanity. The understanding of the principles posed by the theory of relativity gave rise to the atomic bomb.
Quantum mechanics
It is a branch of Physics that studies the behavior of matter at the level of the atom, its particles and its energy. One of its precursors was Louis de Broglie, through his discovery of the wave and particle nature of physical objects, around 1925. From this area of Physics, quantum effects related to the impossibility of accurately and simultaneously determining the speed and position of a particle are also discovered.
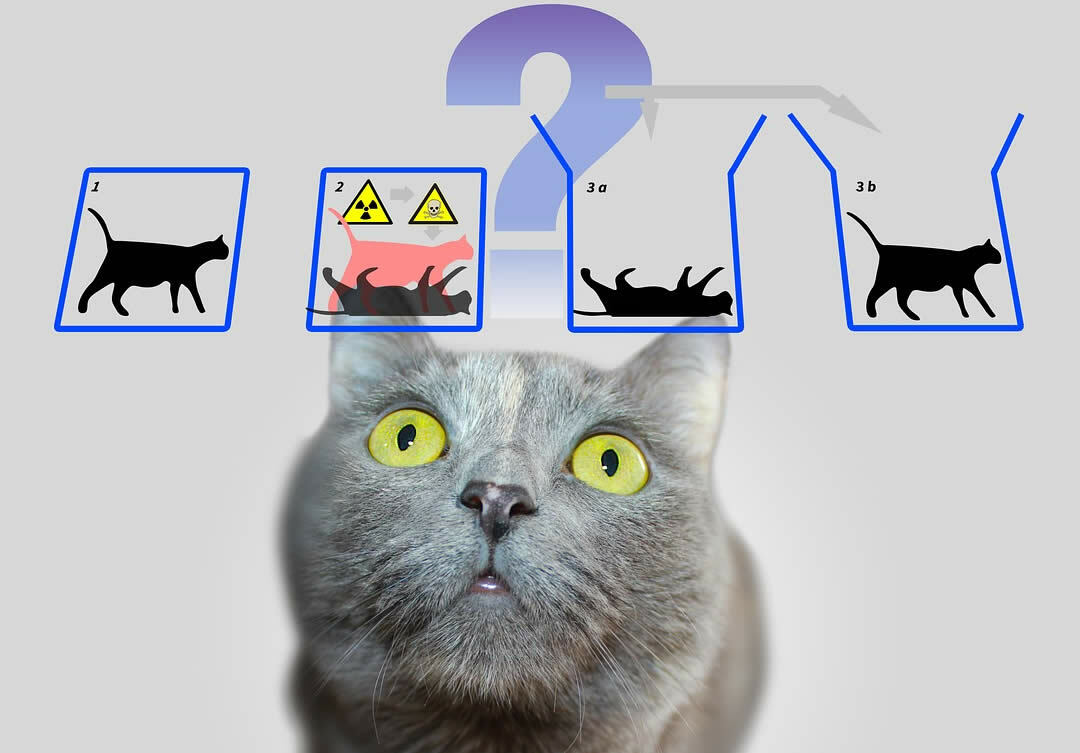
One of the most famous thought experiments in quantum mechanics is about Schrödinger's cat, which in simple terms posits that, as long as we do not look inside the box, the feline is in superposition between the condition of being alive and dead.



