10 Uses of Nylon: Properties and Characteristics
Chemistry / / October 05, 2023
Nylon is a thermoplastic polymer, created from chemical reactions between adipic acid molecules and hexamethylenediamine. These two compounds are combined in a process called polycondensation to form a linear polymer known as a polyamide.
Adipic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H10O4, while hexamethylenediamine is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H16N2.
These two compounds are combined through a chemical reaction in which the carboxyl groups (COOH) of adipic acid bond with the amino groups (NH2) of hexamethylenediamine. This reaction forms amide bonds (CONH) and gives rise to the nylon polymer chain.
The combination of the compounds and the resulting molecular structure of nylon give it its characteristics distinctive physical and chemical characteristics, such as its strength, flexibility, and ability to resist wear and tear. abrasion.
Article content
- • The 4 Properties of Nylon:
- • 11 Characteristics of Nylon
- • Chemical Characteristics of Nylon:
- • Physical Characteristics of Nylon:
- • 10 Uses of nylon:
- • Chemical structure of Nylon
The 4 Properties of Nylon:
Endurance: Nylon is recognized for its high wear and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring durability.
Flexibility: Although it is strong, nylon is also flexible, allowing it to adapt to different shapes and uses.
Low friction: Nylon has low internal friction, making it a suitable material for bearings and moving parts.
Abrasion resistance: Thanks to its molecular structure, nylon can withstand abrasion caused by repeated friction, making it suitable for textiles and ropes.
11 Characteristics of Nylon
Chemical Characteristics of Nylon:
Thermoplastic polymer: Nylon is a thermoplastic polymer, meaning it can be melted and molded repeatedly without losing its chemical properties.
Polycondensation reaction: Nylon is formed through a polycondensation reaction between adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine. This chemical reaction results in the formation of amide bonds, which are responsible for the molecular structure of nylon.
Chemical stability: Nylon is chemically stable under normal conditions, meaning that it does not decompose easily in the face of common chemical agents such as dilute acids, alkalis and organic solvents.
Physical Characteristics of Nylon:
Strength and rigidity: Nylon exhibits high strength and rigidity, making it able to withstand loads and stresses without deforming or breaking easily.
Melting point: Nylon has a relatively high melting point, which gives it good dimensional stability even at elevated temperatures.
Low density: Despite its resistance, nylon has a low density, which makes it a light and easy to handle material.
Flexibility: Nylon is flexible and can be molded into different shapes and sizes without losing its structural integrity.
High wear resistance: Due to its molecular structure, nylon exhibits high resistance to wear and abrasion, making it suitable for applications requiring long-term durability.
Low moisture absorption: Nylon has a low moisture absorption capacity, meaning it maintains its physical properties even in humid environments or with exposure to liquids.
Transparency: Some types of nylon have high transparency, making them suitable for applications such as films and packaging.
UV resistance: Nylon exhibits good resistance to degradation caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
10 Uses of nylon:
Clothing and textiles: Nylon is used in the manufacture of tights, sportswear, swimsuits and heavy-duty garments.
Guitar Strings and Strings: Due to its durability and abrasion resistance, nylon is widely used in the manufacture of musical instrument strings and climbing ropes.
Toothbrushes: Nylon filaments are used in the manufacture of toothbrushes due to their flexibility and cleaning ability.
Bags and backpacks: Bags and backpacks made from nylon are lightweight, water-resistant, and durable, making them a popular choice for everyday use or outdoor activities.
Tires: Nylon is used in the inner casing of tires to provide strength and durability.
Broom bristles: Nylon bristles are used in brooms due to their ability to pick up dust and dirt effectively.
Packing material: Nylon is used in the manufacture of packaging films and bags due to its strength and moisture barrier.
Gears and bearings: Nylon is used in the manufacture of gears and bearings due to its low coefficient of friction and wear resistance.
3D printing filaments: Nylon is used as a 3D printing material due to its durability and ability to produce objects with high precision.
Clotheslines: Clotheslines made of nylon are lightweight, strong and do not corrode, making them ideal for outdoor use.
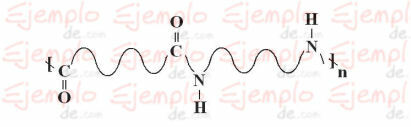
Chemical structure of Nylon
The chemical structure of nylon is as follows:
How to cite? Contreras, V. & Del Moral, M. (s.f.). Uses of Nylon.Example of. Retrieved on October 4, 2023 from https://www.ejemplode.com/38-quimica/3074-usos_del_nylon.html



