Examples of Subatomic Particles
Examples / / November 09, 2023
The subatomic particles are those that are smaller than the atom, some belong to the atom and others do not. For example: electrons and protons, that belong to the atom, and neutrinos and bosons, that do not belong to the atom.
Almost all known subatomic particles are unstable and are not found on planet Earth under normal conditions. These particles are usually very difficult to produce or usually break down into other particles.
Subatomic particles are produced when cosmic rays collide with atoms in Earth's atmosphere. Additionally, many subatomic particles are produced in particle accelerators.
- See also: Molecules
Types of subatomic particles
- Elementary particles. They are the fundamental particles that constitute matter. As far as is known, they are not made up of smaller particles, nor has their internal structure been studied. For example: leptons and quarks.
- Composite particles. They are particles that are made up of several elementary particles, which together constitute a linked state stable (state in which a particle has a certain potential energy that makes it stay in a region of the space). For example: electrons and protons.
- Virtual particles. They are particles that exist for such a short period of time that it is not possible to measure their properties according to the Heisenberg indeterminacy principle. For example: virtual bosons and virtual photons.
The Heisenberg indeterminacy principle or uncertainty principle establishes that, according to quantum physics, there is no can simultaneously determine some pairs of physical variables, for example, the linear momentum and the position of a particle.
Examples of subatomic particles
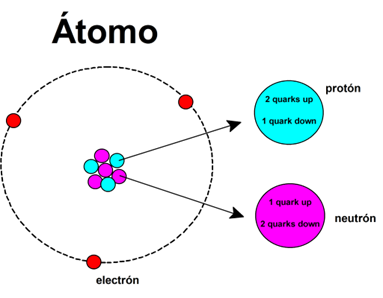
- protons. They are subatomic particles formed by two up quarks (quarks with an electric charge equal to 2/3 of the charge of the electron) and a down quark (quarks with an electric charge equal to -1/3 of the charge of the electron). Protons have a net positive charge equal to 1.
- Neutrons. They are subatomic particles made up of two down quarks and one up quark. Neutrons have a net charge equal to zero.
- Electrons. They are elementary subatomic particles. They have a negative net charge equal to -1.
- Quarks. They are elementary subatomic particles, and they make up the particles that make up the atom. They interact with the four fundamental forces (strong nuclear force, electromagnetic force, weak nuclear force, gravitational interaction).
- Neutrinos. They are elementary subatomic particles. They have zero charge and very little interaction with other particles. Several types of neutrinos are known:
- electron neutrino
- muon neutrino
- tauonic neutrino
- Bosons. They are elementary subatomic particles. They are carriers of fundamental interactions.
- pine nuts. They are subatomic particles made up of a quark and an antiquark.
- Gluons. They are elementary subatomic particles. They are carriers of strong nuclear interactions.
- Photons. They are elementary subatomic particles. They are responsible for the quantum behavior of electromagnetic radiation.
- virtual photons. They are elementary subatomic particles, just like real photons. Real photons are associated with electromagnetic radiation, such as light and X-rays, while Virtual photons are associated with the electromagnetic interaction between charged particles electrical.
- Positrons. They are elementary subatomic particles. They are the antiparticles of the electron and have a positive charge equal to 1.
- Hadrons. They are those subatomic particles made up of several quarks. They can be divided into:
- Baryons. They are hadrons made up of an odd number of quarks.
- Inns. They are hadrons made up of an even number of quarks.
The atom
The atom is the smallest part of matter that still retains the properties of the chemical element to which it belongs. It is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons attached to this nucleus. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons.
In the past, when the first atomic models were proposed, it was considered that the only particles that make up the atom were protons, neutrons and electrons. But with the study of the internal structure of these subatomic particles, it was discovered that some are composite particles. Protons and neutrons are made up of quarks and gluons, while electrons are elementary subatomic particles of the lepton group.
Follow with:
- Ions
- Isotopes
- Biomolecules
References
- Solbes, J., Calatayud, M. L., Climent, J., & Navarro, J. (1987). Conceptual errors in quantum atomic models. Science Teaching: journal of research and teaching experiences, 189-195.
- Domenech Carbo, M. (2013). Physico-chemical principles of the materials that make up cultural assets. Editorial Universitat Politècnica de València.
- Cobián, J. (2018). The standard model of particle physics. Spanish Nuclear Society, 1-13.