Food Chain Example
Biology / / July 04, 2021
Called food chains or food chain to the interaction that exists between living beings for food. It consists of a cycle where energy and nutrients are transmitted from one to another. A simple example: Plants take energy from the sun and transform it through photosynthesis, these plants serve as feed for cows, these cows are used by humans to produce milk and milk is consumed by humans.
The food chain is carried out exclusively between living beings, beginning in plants and eventually reaching higher carnivores.
Food chain categories:
The food chain has been separated into three main categories:
- Autotrophs
- Heterotrophs and
- Saprophytes
These categories have been cataloged as trophic levels, for more information click on the link: Trophic levels example.
Autotrophic Organisms:
Autotrophs, which are also called producers, are the organisms that absorb nutrients directly from the land, air and water, according to their ecosystem, but they do not feed on other beings alive.
These are made up of:
- Most of the vegetables along with their fruits in the terrestrial environment (carnivorous plants are included)
- Phytoplankton in the water.
Heterotrophic Organisms:
These are the organisms that feed on other living beings and have been sub-cataloged in three orders:
First-order consumers.- These are the ones that feed on autotrophs (plants and algae) and are herbivores:
- Insects
- Rodents
- Large mammals: Goats, sheep, horses, cows and
- Birds, which feed on plants and seeds.
Second-order consumers.- These are the hunters that feed on herbivorous animals, fish and insects, highlighting:
- Canines
- Felines
- Seals
- Penguins
- Tuna
- Dolphins
- Whales
- Ducks
- Swans
- Herons etc.
Third-order consumers.- These are made up of animals that feed on both herbivorous animals and other carnivores and are divided into two:
- Hunters and
- Scavengers
Hunters are:
1.- The big cats.- Tigers, lions, leopards etc.).
2.- Hunting birds.- Eagles, owls.
3.- Sailors.- Sharks and killer whales.
Scavengers are:
1.- Birds.- vultures, bone-breakers, buzzards, condors.
2.- Mammals.- Hyenas, badgers.
3.- Reptiles.- Comfortable dragons.
Saprophytic organisms:
These are bacteria and worms, which are the ones that decompose organic matter, both animal and vegetable, taking the nutrients and converting them into matter with nutrients that ends up in the earth, starting the cycle of the chain again food.
Note: There are organisms that in some ecosystems can act as first-order consumers and in others, as second or third-order consumers. This happens for example with pigs. They are generally herbivorous pachyderms, and they are treated that way on farms. However, in many natural ecosystems, when there is a shortage of plants they act by hunting small animals (second-order consumers), although most often they act as scavengers (third-order consumers) order).
Omnivorous Organisms:
This category is in the third to heterophores and omnivores are living beings that feed on plants and animals, hunting and gathering, here the human being stands out, who remains as a tertiary consumer but encompasses the two orders main.
Food chains can be studied from a group of species or from the animals and plants that inhabit an ecosystem.
Example of the food chain in dolphins:
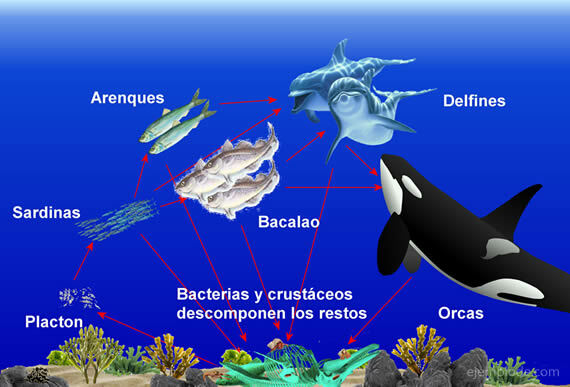
Dolphins are cetacean mammals that inhabit the seas, they are carnivorous animals and are considered third-order hunters.
The dolphin food chain can be located as follows:
Producer organizations: Plankton and some algae.
Primary consumers: Herrings, sardines, crustaceans.
Secondary consumers: Cod, Squid, octopus, penguins.
Third order consumer: The dolphin, which consumes both secondary consumers and primary consumers. The dolphin can be eaten by Orcas and Giant Sharks.
Decomposers. When dolphins die, they are consumed by small crustaceans that are part of the plankton, and by bacteria that are found at the bottom of the sea.
Example of a food chain in a lake ecosystem:
Lake Pátzcuaro is located in the state of Michoachán, and is famous for the fish that are caught there, especially charales and white fish. Lake Pátzcuaro forms a freshwater aquatic ecosystem, in which the elements of the food chain can be identified:
Producer organizations: Algae, roots of some plants and phytoplankton.
Primary consumers: zooplankton and insect larvae.
Secondary consumers: Charales
Tertiary Consumers: White fish, tilapia, carp. These are consumed by humans.
Decomposers. When they die, the remains of animals and plants are decomposed by plankton and bacteria found at the bottom of the lake.

