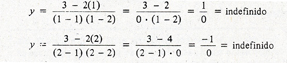Example of Dependent Variable and Independent Variable
Math / / July 04, 2021
The values of X represent elements of the domain and those of y elements of the path. Another way to name them are: x independent variable, and dependent variable because its value depends on the value chosen for x.
In algebra it is common to use literal values for variables, so it is important to have understood the definitions and floating of the functions, so as not to have difficulties with this type of problems.
Let the correspondence rule be r: r (x) = x2 + 2x
r (2) = 22 + 2(2)=8 (2, 8)
r (a) = a2 + 2a, (a, a2 + 2a)
r (a + 1) = (a + 1)2 + 2 (to + 1)
= a2 + 2a + 1 + 2a + 2
= a2+ 4a + 3, (a + l, a2+ 4a + 3)
The domain, the path, and the correspondence rule define a function; Before we said the function defined by 2x + y = 3, are we contradicting ourselves? This is not really the case, what happens is that for practical reasons the domain and the route are not explained and only the correspondence rule is given, considering that it was clarified beforehand that we work in the field of royal iúnieros, so that whoever "reads" the correspondence rule can, from there, determine the domain and the route, although this is not always easy. In these cases e says that both domain and path are implicit in the correspondence rule.
2x + y = 3 or y = 3-2x
The value of x must be a real number to which another real number will correspond. If we observe the expression on the right side of the equality we observe that the instruction or proposition it represents tells us that the product 2x is subtracted from the number 3, as these operations are binary in R, we will always obtain another element of R if X R, that is, yER, then the domain is formed by all R and the path will also be R.
y = x2
Any real number for x gives us another real for y, so the domain is R, but since x2 > Or, the path will be positive numbers or zero.
y = 3 - 2x / (x-1) (x-2)
In the numerator or in the denominator, any real number for x gives us another real number, but since the division between O is not defined, the values 1 and 2 for x, y in general, the values of x that make O to a denominator do not find a real number that corresponds to them and therefore they are not elements of the domain.
EXAMPLE OF INDEPENDENT AND DEPENDENT VARIABLE: