Example of Human Body Bones
Biographies / / July 04, 2021
The bones of the human body or osseous system It is the one in charge of the support and motor functioning of the body and in the case of humans it is formed per approximately 206 bones (this may vary in children who have split bones that fuse at the grow up).
There are many divisions that have been made according to their size and function:
- Short
- Long and
- Blueprints.
Due to their training, they are divided into:
- Fluffy fabric
- Nutritive adipose tissue and
- Hard tissue
Bones have a posterior division called skeletal regions. The one that is separated into:
- Axial function bones
- Appendicular function bones
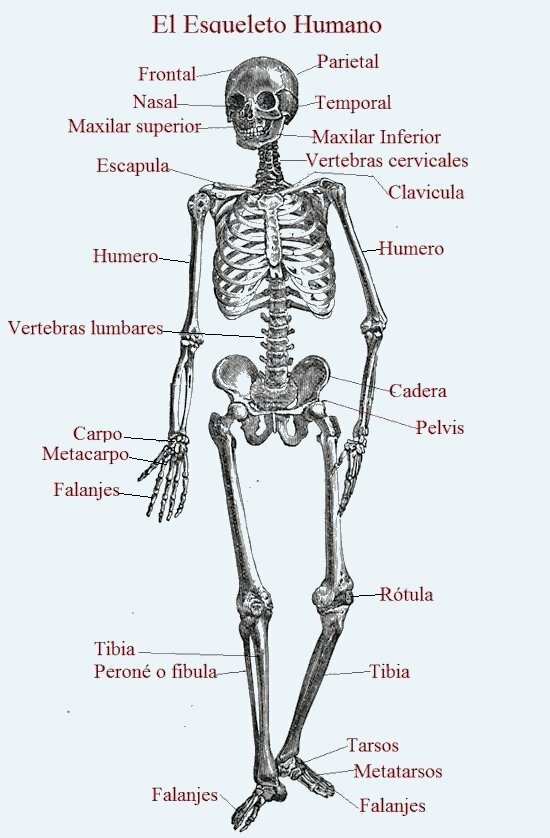
The bones of the body are:
The first of the divisions of the bones found as follows:
Short bones
They are found in small units such as the spinal column, the wrists, and the mass of the heels. (ankles), including the bones of the ears and some of the bones of the skull (which are fused later).
Long bones
These bones form the motor structure of the body, which although it includes small bones, are part of the extensors, allowing walking and moving the hands.
Flat bones
Flat bones are placed in the body in order to protect organs, the protective function can be seen in the ribs, and the skull.
Bone formation
In its internal structure, bones are made up of:
- Cartilage.- This is a very resistant mass of bone tissue that can be elastic, it also works as a cushion in the joints.
- Bone marrow.- It is a nutritive substance that forms red blood cells or becomes an energy reserve.
- Periosteum.- This is a membrane that covers the bone is very fibrous and resistant, in the region of the ligaments there there is periosteum, this periosteum has blood vessels and nourishes the bone by membranes and blood vessels.
- Tissue.- This has a subdivision because here its structure is reclassified, having the compounds, compact, haversian and spongy.
Fluffy fabric
This tissue is composed of the red bone marrow, where stem cells are found that allow the bone to be repaired and have information genetics, this allows a certain homeostasis that regulates the body in addition to producing red blood cells that pass directly into the stream blood.
Fatty and nutritive tissue
This is an energy reserve in which a very high amount of protein is stored, it appears as a yellow and very dense fat.
This tissue allows the body to store nutrients necessary for growth, sustenance, and formation of blood and red blood cells.
Hard tissue
It forms the base that supports the body, its structure is firm and later it is porous so that the nerves and blood vessels are irrigated and grown.
Compact bone tissue
This tissue is made up of small lamellae, which when put together form the hard outer part of the bones.
Haversian bone tissue
They form cells similar to those of bees, which allow the passage of vessels, nerves and nutrients.
Functions of bones
Sustenance
The main function is the support, which has the quality of supporting the body, without it we would be a mass to form or an exoskeleton would have developed as happens with insects.
Movement
They allow movements, since by inserting the muscles in the legs, hands and various parts of the body, they allow them to be stimulated and movement to occur.
Increase
Growth is divided into two parts
- Throughout.- This is done in the metaphysis, which has growth cartilage.
- In thickness.- In the periosteum, new bone membranes are formed and repaired in case of rupture or damage.
Bones of the human skull:
Right nasal turbinate
Left nasal turbinate
Sphenoid
Right stirrup
Left stirrup
Ethmoid
Frontal
Hyoid
Malar or right zygomatic
Malar or left zygomatic
Right hammer
Left hammer
Lower jaw or mandible
Right upper jaw
Left upper jaw
Right nasal
Left nasal
Occipital
Right palatine
Left palatine
Right parietal
Left parietal
Temporary right
Left temporal
Unguis or right lacrimal
Unguis or left lacrimal
Vomer
Right anvil
Left anvil
Bones of the spine:
Sacrum formed by 5 welded vertebrae
Coccyx formed by 4 or 5 fused vertebrae
C1 cervical vertebra = Atlas
C2 = Axis cervical vertebra
C3 cervical vertebra
C4 cervical vertebra
C5 cervical vertebra
C6 cervical vertebra
C7 = Prominent cervical vertebra
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T1
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T2
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T3
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T4
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T5
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T6
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T7
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T8
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T9
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T10
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T11
Dorsal or thoracic vertebra T12
Lumbar vertebra L1
Lumbar vertebra L2
Lumbar vertebra L3
Lumbar vertebra L4
Lumbar vertebra L5
Bones of the rib cage or thorax:
Breastbone
Left true rib attached to T1 vertebra and sternum
Right vendor rib attached to T1 vertebra and sternum
Left bandage rib attached to T2 vertebra and sternum
Right bandage rib attached to T2 vertebra and sternum
Left bandage rib attached to T3 vertebra and sternum
Right bandage rib attached to T3 vertebra and sternum
Left bandage rib attached to T4 vertebra and sternum
Right vendor rib attached to T4 vertebra and sternum
Left bandage rib attached to T5 vertebra and sternum
Right vendor rib attached to T5 vertebra and sternum
Left bandage rib attached to T6 vertebra and sternum
Right vendor rib attached to T6 vertebra and sternum
Left bandage rib attached to T7 vertebra and sternum
Right bandage rib attached to T7 vertebra and sternum
Left false rib attached to T8 vertebra and anterior rib
Right false rib attached to T8 vertebra and anterior rib
Left false rib attached to T9 vertebra and anterior rib
Right false rib attached to T9 vertebra and anterior rib
Left false rib attached to T10 vertebra and anterior rib
Right false rib attached to T10 vertebra and anterior rib
Left floating false rib attached to T11 vertebra
Right floating false rib attached to T11 vertebra
Left floating false rib attached to T12 vertebra
Right floating false rib attached to T12 vertebra
Bones of the pectoral arch and hands:
Left shoulder blade or scapula
Right shoulder blade or scapula
Left clavicle
Right clavicle
Left humerus
Right humerus
Left ulna
Right ulna
Left radius
Right radius
Left scaphoid
Right scaphoid
Left lunate
Right lunate
Left pyramidal
Right pyramidal
Left pisiform
Right pisiform
Left hook
Right hook
Big left
Big right
Left trapezoid
Right trapezoid
Left trapezius
Right trapezius
Finger bones:
Metacarpus 1 left thumb
Pastern 1 right thumb
Left thumb phalanx 1
Phalanx 1 of the right thumb
Left thumb phalanx 2
Phalanx 2 of the right thumb
Metacarpus 2 left index
Metacarpus 2 right index
Left index phalanx 1
Right index phalanx 1
Left index phalanx 2
Right index phalanx 2
Left index phalanx 3
Right index phalanx 3
Metacarpus 3 left heart
Pastern 3 right heart
Left heart phalanx 1
Phalanx 1 of the right heart
Left heart phalanx 2
Phalanx 2 of the right heart
Phalanx 3 of the left heart
Phalanx 3 of the right heart
Metacarpus 4 annular left
Metacarpus 4 right annular
Left ring phalanx 1
Right ring finger phalanx 1
Left ring phalanx 2
Right ring finger phalanx 2
Left ring phalanx 3
Right ring finger phalanx 3
Metacarpus 5 left little finger
Metacarpus 5 right little finger
Left little finger phalanx 1
Phalanx 1 of the right little finger
Phalanx 2 of the left little finger
Phalanx 2 of the right little finger
Phalanx 3 of the left little finger
Phalanx 3 of the right little finger
