Chemical Energy Example
Chemistry / / July 04, 2021
The Chemical energy is that which comes from chemical reactions. The interaction between chemical species generates breakage and / or generation of bonds, which implies a release or absorption of Energy, respectively. Chemical Energy is called the released energy, which can be used as Thermal Energy and Electric Energy, for example.
Energy in Chemical Reactions
Chemical Energy can be obtained in its maximum expression from two main sources: Combustion and Electrolytic Solutions. On the other hand, at the level of the human body, it is possible to obtain energy through the chemical disintegration of food.
Combustion Energy
For example, when the Fuel Methane CH4, the simplest hydrocarbon, begins to burn in the presence of the Oxygen Oxidizer, it will disintegrate, to form Carbon Dioxide CO products.2 and Water H2OR. In addition, the breaking of the bonds of the Hydrogen atoms with the Carbon atoms will release energy in the form of heat.
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2 O (l) ∆H = -212.8 Kcal / mol
Methane combustion equation. The heat of this reaction is represented by ΔH. The negative sign indicates release of Energy. The reaction is Exothermic.
 Methane gas combustion. The reaction is manifested with a flame.
Methane gas combustion. The reaction is manifested with a flame.
Examples of Heats of Combustion of organic compounds at 25 ° C.
Compound |
Formula |
ΔH (Kcal / mol) |
Methane (g) |
CH4 |
-212.80 |
Ethane (g) |
C2H6 |
-372.82 |
Propane (g) |
C3H8 |
-530.60 |
n-Butane (g) |
C4H10 |
-687.98 |
n-Pentane (g) |
C5H12 |
-845.16 |
Ethylene (g) |
C2H4 |
-337.23 |
Acetylene (g) |
C2H2 |
-310.62 |
Benzene (g) |
C6H6 |
-787.20 |
Benzene (l) |
C6H6 |
-780.98 |
Toluene (l) |
C7H8 |
-934.50 |
Naphthalene (s) |
C10H8 |
-1,228.18 |
Sucrose (s) |
C12H22OR11 |
-1,348.90 |
Methanol (l) |
CH3Oh |
-173.67 |
Ethanol (l) |
C2H5Oh |
-326.70 |
Acetic Acid (l) |
CH3COOH |
-208.34 |
Benzoic Acid (s) |
C6H5COOH |
-771.20 |
For a Fuel to provide all the Heat of Combustion of which it is capable, it must be in a gaseous state. As can be seen in the table, liquid benzene contributes a heat of combustion that is 6.22 Kcal / mol less than that released by gaseous benzene. This means that 6.22 Kcal / mol must be invested to make the change from liquid to gas.
Click for more information on the Fuels.
Electrolytic Solutions Energy
An electrolytic conductor is a medium in which one or more ionic species is involved, which is dispersed with its electrical charge, allowing an electrical current to pass through its Constitution. Electrolytic Solutions are Electrolytic Conductors.
Electrolytic conductors include, in addition to electrolyte solutions, Molten salts, and also some solid salts, such as Sodium Chloride NaCl, and Silver Nitrate AgNO3.
Electron transfer occurs by ionic migration, positive and negative, towards the electrodes. This migration involves not only a transfer of electricity, but also the transport of matter from one part of the conductor to another.
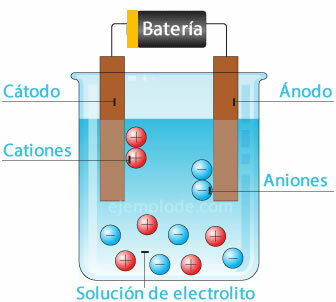 Electrochemical cell
Electrochemical cell
Connecting a potential source to the metallic electrodes (Cathode and Anode), and submerging these in a Aqueous solution, the electrons will travel through the anode, to escape from the solution to the positive pole of the fountain. This is the case, for example, with a Chloride ion, which is released from its electron, and with a neutral charge, it joins another Chlorine atom, to form the diatomic molecule. Chlorine gas will escape from solution.
2Cl- = 2Cl + 2e-
Electrons leaving the negative pole of the source will be housed in the submerged cathode. The species present in the aqueous solution (ions) will take the electrons from the cathode. For example, the Hydrogen ions that make up water, having been in a positive charge, took an electron to be neutralized, and joined with another hydrogen atom to form the molecule diatomic. It will escape as hydrogen gas from solution.
2H+ + 2e- = 2H
2H = H2 (g)
This exchange of electrons can support the operation of car batteries, which consist of Lead Pb electrodes immersed in a solution of Sulfuric Acid H2SW4.
This same energy is obtained in all types of battery that are handled at the domestic level: 9V, AA, AAA, D, to name a few examples.
Food Energy
Human beings assimilate the energy that is released by disintegrating the food we eat in our body. That energy is what our body uses for non-conscious functions (digestion, heartbeat, cellular functions) and those that we carry out.
As long as you do not have intense physical activity and your metabolism is slow, it is advisable to have a regular caloric intake, because foods high in Complex lipids and carbohydrates, which have very large structures, are more difficult to break down, resulting in a reversal of Energy. In that case the effect would be momentarily opposite.
It is advisable to consume fruit when you must work at night, because the fruit contains fructose, a simple carbohydrate that is easy to break down and will have energy available to us after your consumption.
Chemical Energy and its transformations
Thermoelectric plants
Heavy fuels are used in thermoelectric power plants to have a high and long-lasting calorific value. Generally it is Fuel Oil (Fuel Oil). Combustion, which is the chemical stage of the process, will serve as a heating agent for a boiler, which will generate saturated steam. This steam will come out under pressure through the steam distribution network and will begin to move the generator turbines. These devices will be producing Electric Energy to supply the corresponding population.
Chemical Energy → Mechanical Energy → Electric Energy
Automotive Operation
Cars depend on a source of power, which is the Battery. In the battery, electrolytic conduction is already known to occur, which powers the ignition system, dash accessories, and auxiliary power outlets. Thanks to this available electricity, the car will be able to move to take the driver to the desired location.
Chemical Energy → Electric Energy → Mechanical Energy

