Types of Chemical Bonds
Chemistry / / July 04, 2021
When two or more atoms form a molecule, they join together by means of a junction between electrons of its last layers, the most superficial. This union is called Chemical bond. For a chemical bond to form, the atoms must have their incomplete octet, that is, less than eight electrons in their last shell, which is the number that will give them chemical stability.
There are three types of chemical bonds:
- Ionic bonds
- Covalent bonds
- Metal links
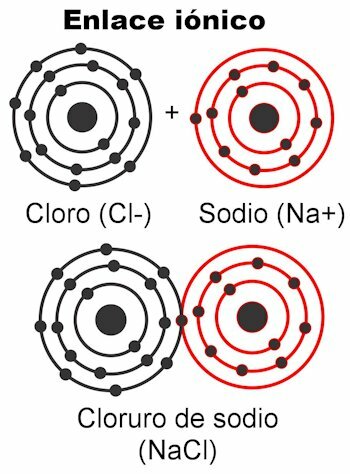
Ionic bonds
Ionic bonds are those in which the valence electrons are attracted by electrostatic forces. The atom (s) that have 1 to 4 valence electrons can deliver them to form the bond; This gives it a positive charge, because it would be getting rid of the negative charges. On the other hand, the atom (s) with 5 to 7 valence electrons will be able to receive the necessary ones to reach 8.
This gives them a negative charge, because they pick up electrons, which are negative. The fact that electrons can be captured or delivered gives the atoms the electrical charge
. According to Coulomb's law, the charges formed on both atoms they are going to attract each other with a force, which is the electrostatics mentioned above. Negative charges attract positive charges and vice versa. Opposite charges attract. Once this force binds them together, the molecule is formed.Ionic bonds occur mostly between metal and nonmetal atoms. Metals give up their electrons and always carry a positive charge, participating as a cation (+). Nonmetals are electron receptors and generally carry a negative charge, participate as anions (-) but it also happens that they carry a positive charge, this when they form groups of charged atoms called radicals, as ammonium NH4+, carbonate CO3-2, phosphate PO4-3.
Among the chemical compounds that are formed by ionic bonds are:
- Binary salts
- Oxisales
When these substances are dissolved in water they dissociate, namely, separate into their electrical charges and these are dispersed in the water together with the hydrogen ions H+ and hydroxyl (OH-) that form water. The mixture that forms is a solution called electrolyte.
- Continue reading: Ionic bond
Covalent bonds
Covalent bonds are those in which electrons are shared without detaching them from the atom, that is, without the formation of electrical charges. The atoms are held together by proximity and use the force with which the nucleus attracts electrons. Once the bond is formed, the two or more nuclei of the atoms end up attracting the shared electrons, thereby fulfilling the octet rule and making the molecule stable.
There are several forms of covalent bonding, and they are:
- Covalent bond
- Coordinate covalent bond
- Polar covalent bond
- Nonpolar covalent bond
The covalent bond It is just like the one described at the beginning. The participating atoms share electrons to all have their complete octet. There are no electrical charges here, because no electrons are shed, they are just shared.
In the coordinate covalent bond it is only one atom that contributes all the electrons necessary for the bond. The other atom simply binds together and takes these electrons as its own. The molecule is formed like this. This is the case, for example, of sulfuric acid H2SW4 in which sulfur shares two pairs of electrons with oxygen atoms.
In the polar covalent bond, the forces between the atoms are tilted to one side of the molecule. This when there are different types of atoms in the molecule. This force is measured in Debye units, and the higher its value on one side of the molecule, the more polar it will be. This means that poles are formed in the structure, and that is why they are given this name. Its forces are asymmetric.
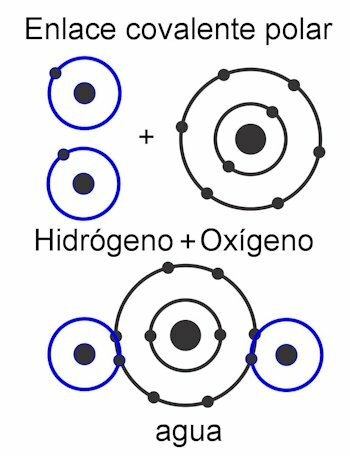
In the nonpolar covalent bond, the forces between the atoms are uniform throughout the entire molecule, and therefore no poles are formed in its structure. It works as a single unit and that is why it is very difficult, almost impossible, to divide its loads. This makes it insoluble in water. This is the case of compounds such as alkanes, which have their equal forces throughout the molecule. Its forces are symmetrical.

- Continue reading: Covalent bond
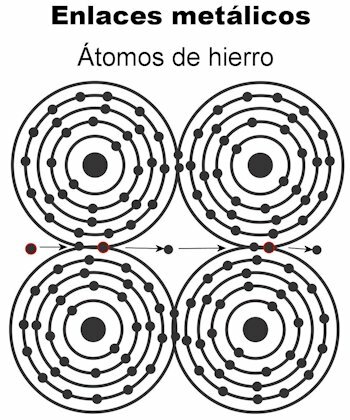
Metallic bond
The atoms of a metal are held together by means of metallic bonds. In this type of bond, the electrons of all the atoms are attracted to form a crystalline lattice that remains firm. The bonds of the crystal lattice have all electrons interspersed and arranged to carry electrical current and heat when it is transmitted to them. In transition metals this structure of metallic bonds is more remarkable, because their atoms are larger.
Examples of ionic bonding
Some substances that have ionic bonds are:
- NaCl sodium chloride. Its ions are Na+ and Cl-.
- Potassium chloride KCl. Its ions are K+ and Cl-.
- Calcium chloride CaCl2. Its ions are Ca+2 and Cl-.
- Magnesium Chloride MgCl2. Its ions are Mg+2 and Cl-.
- Strontium Chloride SrCl2. Its ions are Sr+2 and Cl-.
- Barium Chloride BaCl2. Its ions are Ba+2 and Cl-.
- Aluminum Chloride AlCl3. Its ions are Al+3 and Cl-.
- Na sodium sulfate2SW4. Its ions are Na+ And so4-2.
- Potassium K sulfate2SW4. Its ions are K+ And so4-2.
- Calcium sulfate CaSO4. Its ions are Ca+2 And so4-2.
- Calcium Sulfate MgSO4. Its ions are Mg+2 And so4-2.
- Strontium Sulfate SrSO4. Its ions are Sr+2 And so4-2.
- Barium Sulfate BaSO4. Its ions are Ba+2 And so4-2.
- Na sodium phosphate3PO4. Its ions are Na+ and PO4-3.
- Potassium K phosphate3PO4. Its ions are K+ and PO4-3.
- Magnesium Phosphate Mg3(PO4)2. Its ions are Mg+2 and PO4-3.
- Calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2. Its ions are Ca+2 and PO4-3.
- Aluminum Phosphate AlPO4. Its ions are Al+3 and PO4-3.
- Ferrous Phosphate Fe3(PO4)2. Its ions are Fe+2 and PO4-3.
- Ferric Phosphate FePO4. Its ions are Fe+3 and PO4-3.
Examples of covalent bonding
Some substances that present covalent bonds are:
- Methane CH4.
- Ethane C2H6.
- Propane C3H8.
- Butane C4H10.
- Pentane C5H12.
- Hexane C6H14.
- Heptane C7H16.
- Octane C8H18.
- Propylene CH2= CH2–CH3.
- Acetylene C2H2.
- Methyl alcohol CH3
- Ethyl alcohol C2H5
- Propyl alcohol C3H7
- Isopropyl alcohol CH3CH (OH) CH3.
- 2-propanone or acetone CH3Car3.
- Formaldehyde HCHO.
- Acetaldehyde CH3
- Propionaldehyde CH3CH2
- Butyraldehyde CH3CH2CH2
- Formic acid HCOOH.
Examples of metallic bond
Some substances that present metallic bond are:
- Zinc Zn
- Cadmium Cd
- Copper Cu
- Silver Ag
- Gold Au
- Nickel Ni
- Palladium Pd
- Platinum Pt
- Cobalt Co
- Rhodium Rh
- Iridium Go
- Iron Fe
- Ruthenium Ru
- Osmium Os
- Manganese Mn
- Chromium Cr
- Molybdenum Mo
- Wolfram W
- Vanadium V
- Zrconium Zr
Follow with:
- Atoms
- Ion
- Metals
- No metals
- Alkanes
- Solutions


