Definition of Groundwater
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Javier Navarro, on Sep. 2018
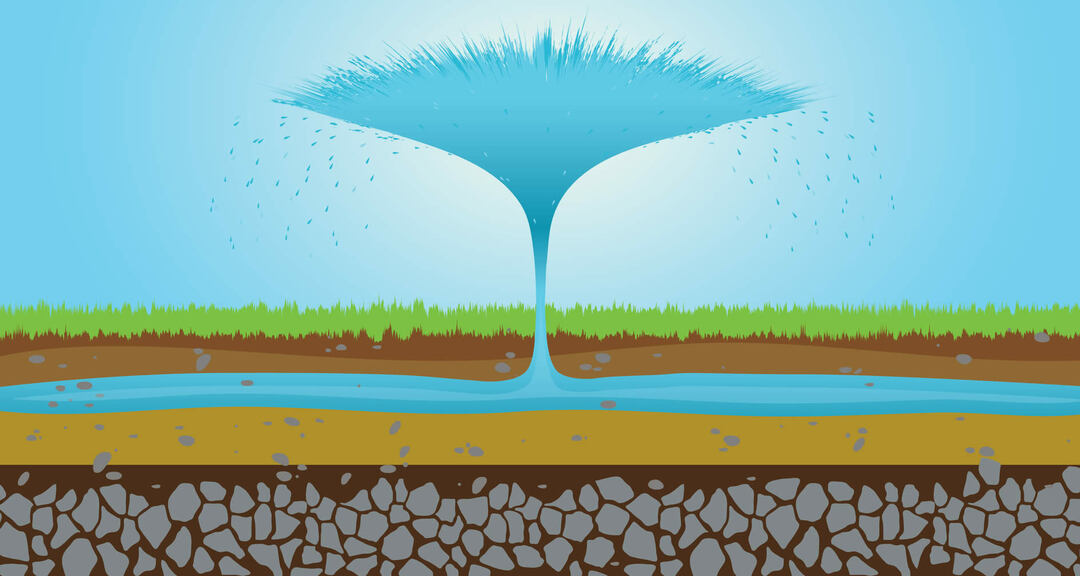 The fall of precipitation ends in the land surface and causes the formation of small streams and rivers. However, a part of the rain seeps into the ground and little by little fissures and cracks are produced that gradually form springs or rivers of Water underground. The areas where water is stored are aquifers. The planet's fresh water reserves are stored in them.
The fall of precipitation ends in the land surface and causes the formation of small streams and rivers. However, a part of the rain seeps into the ground and little by little fissures and cracks are produced that gradually form springs or rivers of Water underground. The areas where water is stored are aquifers. The planet's fresh water reserves are stored in them.
The capture of this resource is of essential importance for human supply. The water found in the subsoil is normally drinkable and thanks to it a third of humanity can drink. It also has agricultural, livestock and industrial uses. His exploitation it has a special value in periods of drought.
In recent years, some aquifers have been recharged by artificial systems to maintain the water table within adequate parameters.
Natural reservoirs with inlet and outlet pipes
For the rain to penetrate the ground, it is necessary that the soil has a type of permeable rock, that is, that allows water to pass through it. When the accumulation of more water is no longer possible because the rock is impermeable, the
aquifer.Aquifers are reservoirs formed spontaneously. Every aquifer has an inflow of water, an outflow and a capacity of storage determined. The entry point originates from infiltrated water. The outlet or discharge takes place in the form of springs or fountains. Storage depends on two factors: the porosity of the ground and its cracking.
Not all aquifers are the same. Some are porous and are formed by loose materials such as sand or gravel. Fissures are formed from firm, consolidated rocks over which water circulates. On the other hand, the degree of water pressure is a determining factor in the typology of the aquifer.
The water in the aquifers is usable for the farming and livestock. However, when the amount of water that is extracted is greater than the natural recharge, there is an overexploitation of the aquifer.
Pollution of aquifers
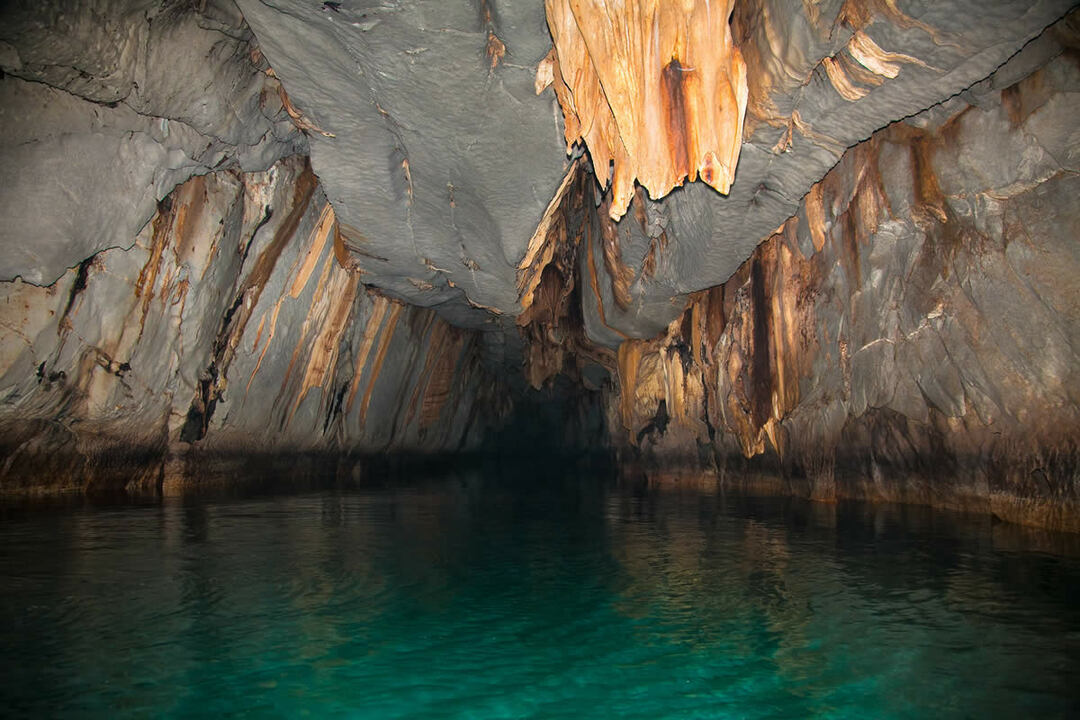 Groundwater can also be contaminated by external agents. The origin of the contamination it is very diverse: sanitation systems, landfills, industrial waste, fertilizers used in agriculture or natural pollutants such as arsenic. The polluting substances reach the aquifers through an infiltration process.
Groundwater can also be contaminated by external agents. The origin of the contamination it is very diverse: sanitation systems, landfills, industrial waste, fertilizers used in agriculture or natural pollutants such as arsenic. The polluting substances reach the aquifers through an infiltration process.
In rivers, water pollution is not so serious, since there is a constant renewal of water. In contrast, polluted groundwater flows very slowly and this circumstance exacerbates the levels of contamination.
Photos: Fotolia - Phuri / Aleksandar Todorovic
Groundwater Topics