Example of Physical Changes
Physics / / July 04, 2021
It is called as physical change to the phenomenon that is produced when bodies alter their characteristics like volume and aggregation state, but without the matter undergoing changes in its structure basic or internal.
In nature there are two types of changes in matter which are:
- Physical changes
- Chemical changes.
Chemical changes. They are those in which one or more substances change their internal structure to form a different substance, with characteristics and properties different from the original substance or substances.
Physical changes. They are those in which the substance changes its shape, its volume or its physical state, but its internal structure does not change, that is, it remains the same substance all the time.
Most of the physical changes are related to temperature.
Aggregation state changes are the best known. Matter and each substance in particular, can have any of the following states: solid, in which the Substances have their own shape, their molecules are tightly bound, and have little movement between they. The liquid state the substance acquires the shape of the container that contains it, the molecules are united, but it can flow, since its molecules can slide over each other. In the gaseous state the substance acquires the shape of the container that contains it, the molecules are very little attached to each other, and move very freely, in addition to tending to occupy the entire volume of the container that contains.
The physical changes are:
Most substances can change from one state of aggregation to another.
- Solidification: It is when a liquid body goes to the solid state.
- Fusion: When a solid body goes to the liquid state.
- Evaporation: When a liquid goes to the gaseous state.
- Condensation: When a gas goes to the liquid state.
- Positive sublimation: When a solid body goes to the gaseous state.
- Reverse sublimation: It is when a gas goes directly to the solid state.
There are other changes in which the state of aggregation of matter is not modified, but other characteristics are modified, such as density or volume:
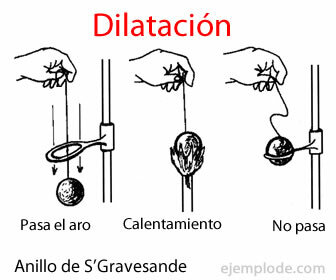
- Dilatation: It is when a body acquires a greater volume. This generally happens when the temperature increases.
- Contraction: In contraction a body decreases its volume, which usually happens when the temperature decreases.
- Deformation: When a body changes or its shape is altered, mainly by mechanical action.
- Break: When a mechanical action causes the molecules of a body to separate and break, that is, they lose their cohesion.
- Elongation: It is a type of deformation in which bodies are stretched.
Examples of physical changes:
- Solidification: Freezing water: ice cubes in the refrigerator.

- Evaporation: The steam produced by boiling water.

- Condensation: When water vapor is passed in an alembic, to obtain distilled water.

- Positive sublimation: Dry ice (solid carbon dioxide), goes directly from solid to gaseous state.

- Reverse sublimation: When a solution of acetic acid (vinegar) is boiled, the acetic acid vapors on cooling turn into solid crystals.

- Fusion: It is when an ice cream or popsicle melts while we are eating it.

- Dilatation: This is what happens when a tire gets hot on the road. As the air inside heats up, the air expands, and the pressure inside the tire increases.
- Contraction: When we hit a wood with a hammer, it leaves an area in the shape of the head of the hammer, where the wood in that area is more compressed than in the rest of the wood.

- Deformation: It is what happens when a car collides, that due to the impact its parts lose their shape.

- Elongation: This is what happens when we stretch a gum, which increases its length without breaking.

- Break: If we apply pressure to a wood resting on its ends, it will first deform, curving. Passing a certain point, the wood does not support any more pressure and will break.

