Example of Watt's Law
Physics / / July 04, 2021
Electrical appliances and circuits consume a certain amount of energy while receiving a supply of electricity, which they use to do work. In many non-circuit breakers, such as televisions, there is an always-on remote start circuit, and the rest is dissipated in the form of heat and electromagnetism. This consumption is called power. This power consumption is determined by the resistance of the circuit or appliance, the input voltage and the current it uses.
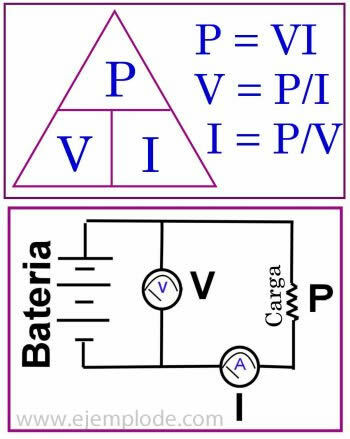
Watt's law is stated as follows:
The power consumed is directly proportional to the voltage supplied and the current flowing.
The unit of power is the Watt, and it is the product of the circuit voltage and the amperage:
P = VI
V = P / I
I = P / V
The most commonly used multiples are the kilowatt (kW), and the milliwatt (mW).
When power consumption is calculated in relation to time, to express continuous consumption, then the unit called Watt hour (W / h) or its multiples is used the kilowatt hour (kW / h) and the milliwatt hour (mW / h).
E = Pt
P = E / t
t = E / P
Examples of Watt's Law
Example 1:
Calculate the power of an electric motor that has a supply of 120 Volts and a current of 3.5 Amps.
P =?
V = 120 V
I = 3.5 A
P = VI
P = (120) (3.5) = 420 W
The power consumed is 420 Watts
Example 2:
Calculate the voltage received by a circuit that consumes 4 W, with a current of 150 mA.
P = 4 W
V =?
I = 150 mA = 0.15 A
V = P / I
P = (4) / (0.15) = 26.66
The circuit voltage is 26.66 V.
Example 3:
Calculate the amperage that circulates through a 75 W bulb, with a voltage of 120 V, and its consumption during 15 minutes.
We calculate the amperage:
P = 75 W
V = 120 V
I =?
I = P / V
P = (75) / (120) = 0.625
The bulb circuit current is 0.625 A.
Now we calculate the consumption:
E = Pt
E =?
P = 75 W
t = 15 minutes = 0.25 hours.
E = Pt
E = (75) (0.25) = 18.75
The consumption of the bulb is 18.75 W / h, equal to 0.01875 kW / h.



