What Does Hormones Mean?
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
The Hormones are chemicals who are in charge of assist the development and well-being of the human body. They are created in it, thanks to the glands, indispensable organs without which the body would not last long alive.
General Characteristics of Hormones
There are different organs in the human body whose secretions pass directly into the blood, influencing the functioning of the organs. These organs are known as Internal Secretion Glands or Endocrine Glands for not having conduits through which secretions pass into the circulatory stream.
The active constituents of these secretions, which have very marked physiological properties are called Hormones, word for Greek etymology meaning "I excite". Hormones exert a regulatory function in the body, being essential for its proper functioning.
The removal of any of the endocrine glands causes serious disorders in the body and in some cases, even death.
The most important endocrine glands are the digestive system, not currently considered, the pancreas, the thyroid and parathyroid glands, the adrenal glands, the sexual organs, and the pituitary.
Hormones of the Digestive System
In the mucosa of the pylorus there is a hormone known as Gastrine, which excites the secretion of gastric juice. Its active principle seems to be Histamine.
Three hormones are found in the mucosa of the intestine, the most important being the Secretin, which stimulates the pancreas to produce pancreatic juice.
Pancreas Hormone: Insulin
In certain tissues of the pancreas known as Islets of Langerhans, the hormone is produced that passes directly into the blood, which, even before isolating it, received the name of Insulin. It has the function of regulating the amount of sugars in the blood, supporting the body in its metabolism.

Thyroid Gland Hormone: Thyroxine
Malfunction of the Thyroid gland, found on the neck, causes cretinism. Kendall isolated from the gland the active principle from him that he called Thyroxine. It is administered to patients in whom there is poor secretion from the thyroid gland.
Parathyroid Gland Hormone: Parathormone
The parathyroid glands closely associated with the thyroid gland secrete a hormone, the Parathormone, what regulates the metabolism of calcium in the blood, from calcium in the bones. Its action is similar in this respect to Vitamin D. Tetanus in children appears to be due to abnormal activity of these parathyroid glands.
Hormones of the Adrenal Glands: Adrenaline
The Adrenal or Adrenal Glands they are found on top of each kidney; They are very small, flat, with a diameter of 2.5cm, and a weight of about 3 grams. Its active principle is Adrenaline or Epinephrine.
The Adrenalin acts of vasoconstrictor thereby raising blood pressure. It is the most valuable hemostatic known. It also works by stimulating the heart.
Two products of action similar to adrenaline, but obtained in the laboratory and not in the functioning of the endocrine glands are the Ephedrine and Bencedrine, which are not hormones.

Cortical Hormones
The adrenal glands contain other hormones, located in the cortex of these glands. The lack of these hormones causes Addison's disease, characterized by the tan color of the skin, anemia, low blood pressure and tuberculous degeneration of the adrenal glands.
The corresponding hormones, called curtains, are all derived from Corticosterone, which is a sterol. The most active is Deoxycorticosterone.
The cortex of the adrenal glands also produces various hormones analogous to sex hormones. The Adrenosterone, isolated from the adrenal glands of the ox, has male sex hormone properties.
Sex Hormones
The sex glands they secrete various hormones that determine the development and maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics. They are found simultaneously in both sexes and their names refer only to their specific action and not to their existence. Those that have an influence on the female character are the Estrogen Hormones, which cause a proliferation of the mucosa uterine, the most important being Estrone or follicular hormone, estriol and estradiol, from the urine of the pregnant
In addition, the Hormones Corpus luteum or pregnancy hormones, the most important being the Progesterone. The Stilbestrol it is more active than some of the female hormones.
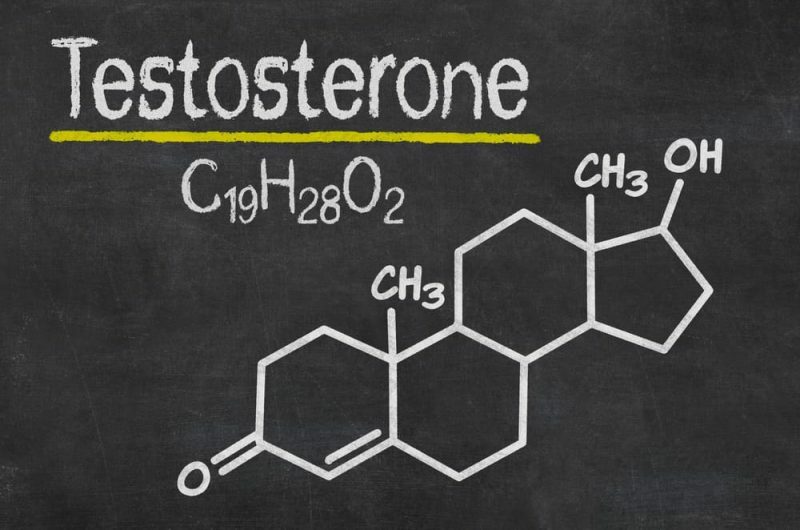
Male or Androgen Hormones are the Androsterone and Dehydroandrosteroneisolated from human urine, the former being the most active, and the latter being the Testosterone, obtained from the bull's testicles, much more powerful than the other two.

Hormones of the Pituitary Gland
The pituitary glandor pituitary It is an organ located at the base of the brain, and it has three parts: Anterior Lobe, Posterior Lobe and Intermediate Section. The removal of the Anterior Lobe stops growth, while if it acts more actively it determines a gigantic development (gigantism and acromegaly).

Vegetable Hormones
At the tips of grass plants, such as oats and corn, substances are produced that diffuse downwards condition their growth. Due to their function in the life of plants, these substances are Vegetable Hormones or Phyto-Hormones, and are called Auxins. Ingested with plant foods, they are eliminated in the urine.
Examples of Hormones
- Gastrine
- Secretin
- Insulin
- Thyroxine
- Parathormone
- Adrenaline or Epinephrine
- Corticosterone
- Deoxycorticosterone
- Adrenosterone
- Estradiol
- Estrone
- Progesterone
- Stilbestrol
- Testosterone