Definition of Cartesian Plane
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in Sep. 2009
 At the request of the math, the plane Cartesian It is a system of references that is made up of two number lines, one horizontal and the other vertical, which intersect at a certain point. The horizontal is called the abscissa or x axis and the vertical axis of the coordinates or the yes, while the point at which they will intersect is called the origin. The main function o purpose of this plane will be that of describe the position of points, which will be represented by their coordinates or ordered pairs. The coordinates will be formed by associating a value from the x axis and another from the y axis.
At the request of the math, the plane Cartesian It is a system of references that is made up of two number lines, one horizontal and the other vertical, which intersect at a certain point. The horizontal is called the abscissa or x axis and the vertical axis of the coordinates or the yes, while the point at which they will intersect is called the origin. The main function o purpose of this plane will be that of describe the position of points, which will be represented by their coordinates or ordered pairs. The coordinates will be formed by associating a value from the x axis and another from the y axis.
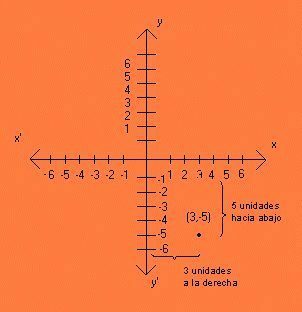
Meanwhile, to locate the points in the Cartesian plane, the following must be taken into account... to locate the abscissa or value of the x, the corresponding units will be counted in direction right, if they are positive and in the left direction, if they are negative, starting from the point of origin which is 0. And then, from where the value of x was located, the corresponding units will be counted up in case to be positive, downwards, in case of being negative and in this way any point is located given the coordinates.
The distance that separates the place from where we are, even for example the place to which we want to go, which, let's say, is four blocks to the north and six to the west, it can be captured through a Cartesian plane, taking as the origin of the plane the one in which we find ourselves U.S.
The origin of the denomination The Cartesian plane as such has been carried out in honor to the renowned seventeenth-century French mathematician and philosopher René Descartes, for having promoted the need to take a starting point on which to build all knowledge.
Topics in Cartesian Plane