Epidural and Spinal Anesthesia
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., in Dec. 2018
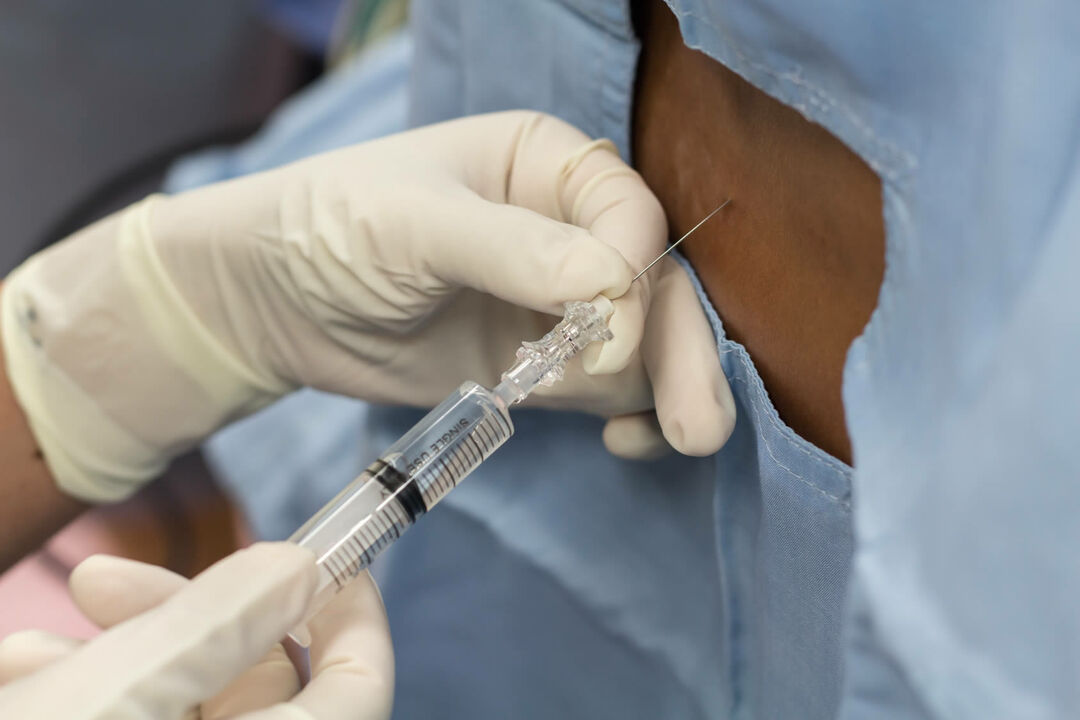
 Anesthesia is used to remove the sensation, both painful and sensitive associated with the performance of a medical procedure, especially surgery.
Anesthesia is used to remove the sensation, both painful and sensitive associated with the performance of a medical procedure, especially surgery.
There are several anesthesia techniques, so the most appropriate will be chosen according to the effect to be achieved. These include local, regional (epidural or spinal) anesthesia in which the conscience, that is, the individual remains awake, and general anesthesia in which the patient falls asleep completely.
Local anesthesia is applied for example to the edges of a wound to suture it, a type of local anesthesia is the trunk, which consists of blocking a nerve to have a greater anesthetic area, is used for example in procedures like hand surgery. In the case of epidural and spinal anesthesia, anesthetics are administered at the level of the spine, while in general it is done intravenously.
In which cases is epidural and spinal anesthesia used?
Both techniques are used to block pain during some types of surgery. Especially in the pelvic, inguinal or lower limbs area.
These techniques are of choice in caesarean sections, uterine or ovary gynecological surgeries, natural childbirth, sterilization, repair of inguinal hernias, appendectomies, traumatic leg surgeries and in patients with contraindications to general anesthesia.
Differences between epidural and spinal anesthesia
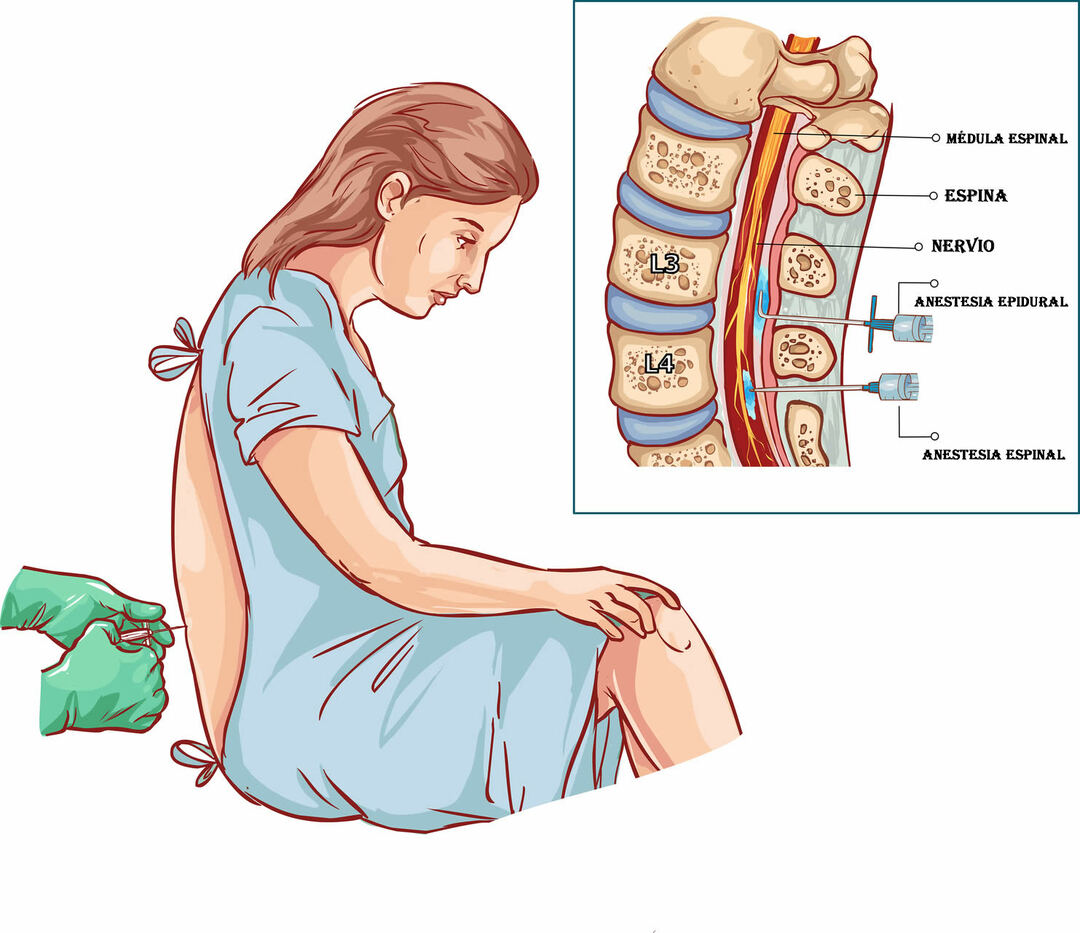
In both cases, anesthesia is applied at the level of the channel spinal, located within the spinal column. The difference lies in the compartment where the anesthetic drugs are applied.
Remember that the medulla, like the brain, is covered by three membranes known as meninges, these are the pia mater, which directly covers the structures of the Central Nervous System, then the arachnoid and more superficially the dura mater.
The subdural space is located between the dura and the arachnoid, while outside the dura, that is, between it and the bone, the epidural space is located.
 During spinal anesthesia, a needle is inserted into the back of the back, between two vertebrae, and directs until reaching the dura mater, crossing it to reach the subarachnoid space, where the anesthetic. In the case of epidural anesthesia, the needle stops before reaching the dura mater, applying the drugs in the epidural space.
During spinal anesthesia, a needle is inserted into the back of the back, between two vertebrae, and directs until reaching the dura mater, crossing it to reach the subarachnoid space, where the anesthetic. In the case of epidural anesthesia, the needle stops before reaching the dura mater, applying the drugs in the epidural space.
The site of app of anesthetics allows for some different effects. In the case of epidural anesthesia, a more selective anesthesia can be done, eliminating the pain while preserving some nerve functions. It is also possible to leave a catheter that allows anesthetics to be applied during the postoperative period.
Spinal anesthesia performs a complete block of nerve functions in addition to the sensitivityIt has a duration of effect that can be shorter and a single application can be made, since it is not possible to leave catheters in the space where it is applied.
Combined anesthesia
In some procedures, epidural anesthesia is combined with general, this is particularly useful in the case of surgeries that merit working in different anatomical areas (for example in plastic surgery) and those where there may be intense pain in the postoperative period (as is the case of surgery to remove the uterus known as hysterectomy).
Photos: Fotolia - Corbacserdar / Samrith
Topics in Epidural and Spinal Anesthesia


