Definition of Golgi apparatus
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., at Mar. 2016
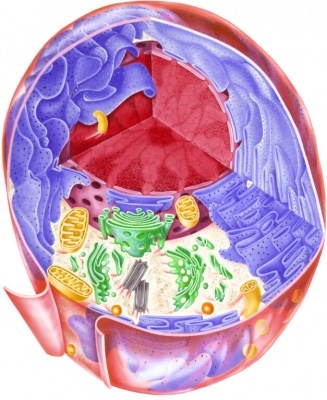
 The Golgi apparatus It is one of the structures that make up the interior of the cells of both animals and plants. It is an organelle that has the shape of a series of attached cisterns that fulfills functions related to the management of protein synthesized in cells.
The Golgi apparatus It is one of the structures that make up the interior of the cells of both animals and plants. It is an organelle that has the shape of a series of attached cisterns that fulfills functions related to the management of protein synthesized in cells.
Once the proteins are produced, they leave the endoplasmic reticulum to enter the Golgi apparatus, a structure in which they finish forming and are well prepared for their storage or for release. This structure is particularly developed in cells that have functions related to the secretion of substances, such as cells of the nervous system that release neurotransmitters or those of the endocrine system that produce hormones.
Structure of the Golgi apparatus
This organelle is located near the nucleus of the cell, it is formed by membranes that are attached one on top of the other in sheets, giving rise to spaces known as cisterns. These membranes maintain their shape thanks to the presence of support structures called microtubules.
The Golgi apparatus is located near the endoplasmic reticulum, in order to capture the proteins that are produced at that level and continue their processing.
This structure is much more complex in animal cells than in plant cells.
Golgi Apparatus Function
The DNA It is the molecule that contains all the information that allows the functioning and replication of cells. This information is translated into proteins that are made by ribosomes from the codes contained in DNA.
 Once processed, the proteins pass to the Golgi apparatus, where they are transported along of a series of cisterns where they are modified to become active forms of the proteins.
Once processed, the proteins pass to the Golgi apparatus, where they are transported along of a series of cisterns where they are modified to become active forms of the proteins.
For this, as they pass through the Golgi apparatus, they receive fragment carbohydrates or lipids thus originating the glycoproteins, glycolipids and lipoproteins. Once this transformation has occurred, they are packaged in membranes that are formed by fragments of the cisterns to originate two types of vesicles, some are the secretory vesicles which are a system of transport with which proteins are carried outside the cell, towards the membrane mobile, to be released and carry out their function; others are the storage vesicles in which proteins remain in the cytoplasm of the cell until the moment they must be released. These storage vesicles are also known as lysosomes.
Photos: iStock - blueringmedia / MedicalArtInc
Topics in Golgi Apparatus
