Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Guillem Alsina González, in Apr. 2017
 Encode the information in digital computer systems and, more specifically, the text, requires an agreement that encompasses all the parties that exchange information so that they can agree on how to represent it.
Encode the information in digital computer systems and, more specifically, the text, requires an agreement that encompasses all the parties that exchange information so that they can agree on how to represent it.
As information and communication technologies evolve, communication in different places simultaneously, and receive contributions from all over the world, several systems of coding of information, more specifically letters, numbers and symbols, although due to the preponderance of the United States in the technological field, the one that ultimately won was ASCII, whose acronym mean American Standard Code for Information Interchange, and consisting of a seven-bit encoding for the alphabet, numbers and symbols common in English texts.
Since computer systems work with sets of eight bits (called bytes), what the inventors did was use the bit that was left over as parity to identify errors in stored information.
The popularization of new technologies and the arrival of
computing to everyone, brought with it the need to represent information in languages other than English, which included characters not contemplated in the code Original ASCII.Thus, and in successive revisions, the ASCII code has been expanded, so that it currently supports up to 95 printable characters, along with 32 non-printable characters.
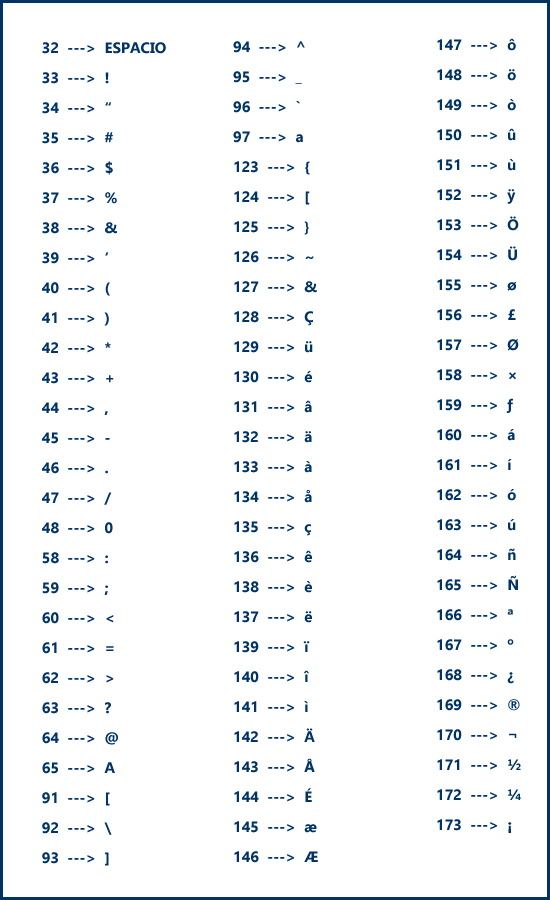
Non-printable characters correspond to control codes that were originally used to instruct devices. such as printers (now not so common anymore) or screens, and that can be used by input devices such as, for example, keyboards.
When counting lowercase letters, uppercase letters, numbers and various symbols (such as square brackets, parentheses, symbols of the four basic operations, period, ...), you are missing the items required to support characters that use the same Latin alphabet as English (such as Spanish, French, Portuguese, or Italian), such as accented letters, ç, or the ñ.
To be able to work with these characters, an extension of the original ASCII is needed, which is often called US-ASCII, since it was born in the United States (US corresponds to United States), which include the set of ASCII codes and characters as well as other additions, being for therefore compatible with ASCII encoded files, but the inverse relationship does not necessarily it happens.
But where did the idea of creating a unified code come from with which to deal with information? Well, of necessity, but for its materialization, they were based on the codes used in telegraphy.
Today, all computers and platforms software, use the ASCII code (or are able to work with it) to receive, to stock, manipulate and share digital information.
Photo: Fotolia - Chris Titze
ASCII Topics


