Definition of Food Chain
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Cecilia Bembibre, in May. 2010
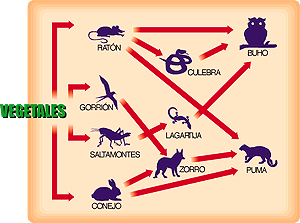 The notion of food chain or trophic chain is used to designate the type of links that are established between different organisms, ties of survival which imply that the strongest eat the weakest and at the same time serve as food for other stronger beings. Food chains can start from microorganisms more insignificant in terms of size and reach huge mammals of tremendous proportions, varying in the amount of elements that link the chain, in the complexity of them, etc.
The notion of food chain or trophic chain is used to designate the type of links that are established between different organisms, ties of survival which imply that the strongest eat the weakest and at the same time serve as food for other stronger beings. Food chains can start from microorganisms more insignificant in terms of size and reach huge mammals of tremendous proportions, varying in the amount of elements that link the chain, in the complexity of them, etc.
Food chains are essential for the survival of all living things. A food chain begins with the process of photosynthesis that vegetables make to live. This process uses elements of the environment like light and water. As simple as they may seem, vegetables and plants are undoubtedly the base of the entire food chain and without them no one could live. mammal, amphibian or reptile. An important part of living beings of greater or lesser size that are known as herbivores are fed from vegetables and plants.
The herbivorous animals will then be food for the strongest, wild or evolved animals, who will also be consuming the nutrients of vegetables and plants. Among the most important carnivorous animals we find the human being, an animal that closes the food chain and is not consumed by any under normal conditions. In many senses, the human being also acts as a great consumer of other living beings, specifically raising them to turn them into food instead of taking them from nature as the rest of the animals.
Depending on the type of elements that compose it and the links that occur between them, food chains can become really very complex. In addition, these links between one element and another are not always linear but can cross each other.
Food Chain Topics


