Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Cecilia Bembibre, in Ago. 2009
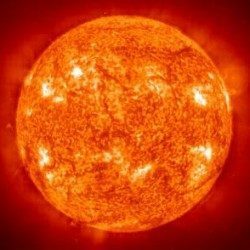 Heat can be defined as Energy resulting from different types of combustion. In the case of the heat that the Earth receives from the Sun, we must then speak of the heat or energy that makes life possible by generating the environmental conditions conducive to it. On the other hand, heat is also understood as sensation related to temperature, sensation that occurs mainly in the summer seasons and that can be described in the languagecolloquial like a suffocating sensation.
Heat can be defined as Energy resulting from different types of combustion. In the case of the heat that the Earth receives from the Sun, we must then speak of the heat or energy that makes life possible by generating the environmental conditions conducive to it. On the other hand, heat is also understood as sensation related to temperature, sensation that occurs mainly in the summer seasons and that can be described in the languagecolloquial like a suffocating sensation.
As energy, heat can be produced by different methods. Among the most common we find chemical and nuclear reactions, the latter being those that take place in the Sun. Other ways to generate heat is through friction (method from which man discovered fire) or the dissipation of electromagnetic waves. Once generated, heat can be transferred to objects or spaces through methods such as convection, radiation, and conduction.
Obviously, the presence of heat on a surface has as a consequence the elevation of its temperature and the consequent
acquisition internal heat. According to the laws of the thermodynamics, the heat of an object or surface is maintained if the heat system of the aforementioned element is closed, as happens for example with the Sun. Heat is also the energy that is transferred from one body to another when leaving that closed system until it reaches a new one.When you speak of heat as the typical seasonal temperature of summer, you are referring to the environmental phenomenon that makes spaces naturally warm without the need for heating artificial. Throughout the last decades, the temperature of Planet Earth has shown important variations, mainly due to the increase in heat and temperatures of its surface and its atmosphere, creating the well-known phenomenon of the greenhouse effect.
Topics in Heat

