Definition of Earth's Crust
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, on Feb. 2009
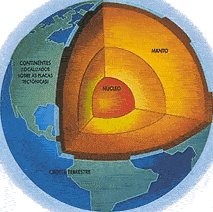 It is known as bark land to the most superficial layer of the planet earth, its thickness varies from 5 km, on the ocean floor and 40 km, in the mountains. Among the most characteristic elements that make up this structure are silicon, oxygen, aluminum and magnesium. Meanwhile, in this, in turn, three layers are distinguished: sedimentary, granitic and basaltic. On the sedimentary side, it is composed of sedimentary rocks that are found only on the continents and in those funds close to the continent.
It is known as bark land to the most superficial layer of the planet earth, its thickness varies from 5 km, on the ocean floor and 40 km, in the mountains. Among the most characteristic elements that make up this structure are silicon, oxygen, aluminum and magnesium. Meanwhile, in this, in turn, three layers are distinguished: sedimentary, granitic and basaltic. On the sedimentary side, it is composed of sedimentary rocks that are found only on the continents and in those funds close to the continent.
In the case of granite, those that compose it are rocks similar to granite that will form the massmother of those continental areas emerged. Between this layer and the next one is located the Conrad discontinuity, which indicates the limits between the granitic and the basalt and finally the basalt, It is made up of rocks similar to basalts, this is the layer that immediately continues to the earth and the Mohorovicic discontinuity separates it from the mantle.
The earth's crust is divided into two types, the oceanic and the continental. The oceanic represents 75% of the surface of the planet earth, it is much finer than the continental one and in it three are recognized levels. The lowest level or level III is made up of gabbros, basic plutonic rocks, and borders the mantle of the Mohorovicic discontinuity. On these rocks is erected the level II basalt rocks, with the same composition than the previous one, then a lower area composed of dikes and the most superficial area of this level is made up of cushioned basalts, which were formed as a result of the solidification of lava with Water oceanic. And on the basalts, then level I will be erected, formed by sediments.
And the continental one has a less homogeneous and dense nature than the previous one, that is why it is located above the oceanic one, since between its composition are rocks that come from various origins, such as acid igneous like granite, accompanied by a important metamorphic rock mass.
Themes in Earth's Crust


