Definition of Cellular Respiration
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in Dec. 2009
A vital process for the survival of living beings
The one with the breathing It is undoubtedly one of the most important processes that living beings develop because it is through it that we can absorb and to expel the air taking part of the substances that compose it and that are so important for the survival of our organism.
When we breathe we absorb air and take part of its substances, and then expel it after having modified it.
Meanwhile, cells, which are those microscopic units that assume an essential role morphologic and functional in living beings, they need respiratory function to guarantee its correct functioning.
Set of biochemical reactions that occurs in most cells and allows cellular nutrition
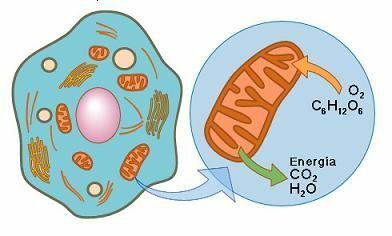 Cellular Respiration is then called the set of biochemical reactions that occurs in most cells. It is considered a very basic process within the nutrition mobile.
Cellular Respiration is then called the set of biochemical reactions that occurs in most cells. It is considered a very basic process within the nutrition mobile.
How is it produced?
In this process, pyruvic acid originated by glycolysis, which is the metabolic pathway responsible for fermenting glucose To produce the energy that the cell needs, it is split into carbon dioxide and water and this gives rise to 38 molecules of ATP.
Putting it in simpler words, cellular respiration is a metabolic process through which cells reduce oxygen and generate energy and water. Without these reactions, cellular nutrition would be impossible.
Cellular Respiration, then, is a part of metabolism, more precisely catabolism, by which the energy found within the different molecules, such as carbohydrates and lipids, will be released in a super controlled way. As respiration occurs, a part of the energy is incorporated into the ATP molecule.
The process takes place in the mitochondria
The process of cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria, which is an organ of the cytoplasm of cells, with a differentiated nucleus, and which deals exclusively with this action.
The mitochondria process oxygen and are in charge of converting the carbohydrates, fatty acids and protein of the foods that are ingested in absolute energy to be able to carry out the most important vital functions.
Two kinds of cellular respiration
Meanwhile, cellular respiration It can be of two types depending on whether oxygen is involved or not. Aerobic respiration makes use of oxygen and turns out to be the most widespread variant (typical of bacteria and those organisms eukaryotes). And the anaerobic respiration, typical of prokaryotic organisms (cells without a cell nucleus), in this type of respiration there is no participation some of the oxygen, but instead some minerals or other by-products of metabolism intervene.
Three-stage process
And the process takes place in three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain.
The first is carried out in the cytoplasm of the cell and corresponds to an anaerobic process, that is, it does not require the presence of oxygen. Meanwhile, the Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria, in the matrix and the intermembrane compartment, and it does demand the presence of oxygen.
And finally, the electron transport chain will be made up of a group of enzymes that are located in the membrane. internal mitochondria, where electrons are accepted and transferred generating a chain that produces energy used to pump. When electrons bond with oxygen, a water molecule is formed.
It is important that we mention that this process is of course important in what corresponds to the physiology of cells but it is also important for people so that we can carry out our daily activities that include physical and mental work and the internal workings of our organs.
Topics in Cellular Respiration