Definition of Carbon Dioxide
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Javier Navarro, in Oct. 2017
 This gas, also known by its chemical formula CO2, is a fundamental element for life on the planet. His molecule It is made up of one atom of carbon and two of oxygen.
This gas, also known by its chemical formula CO2, is a fundamental element for life on the planet. His molecule It is made up of one atom of carbon and two of oxygen.
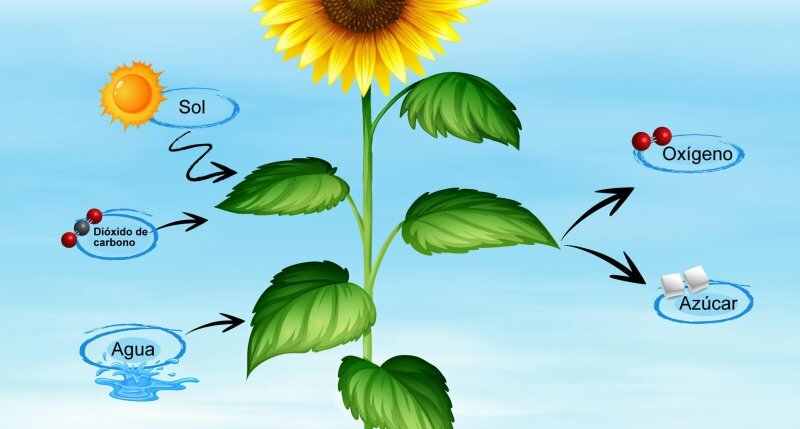
Plants are the creators of CO2
Through the photosynthesis plants carry out carbon fixation. This means that in photosynthesis the inorganic compound of CO2 is transformed into organic compounds Like the carbohydrates. On the other hand, when we breathe we burn carbohydrates to give rise to CO2 and water. In this sense, forests are the best creators of carbon dioxide.
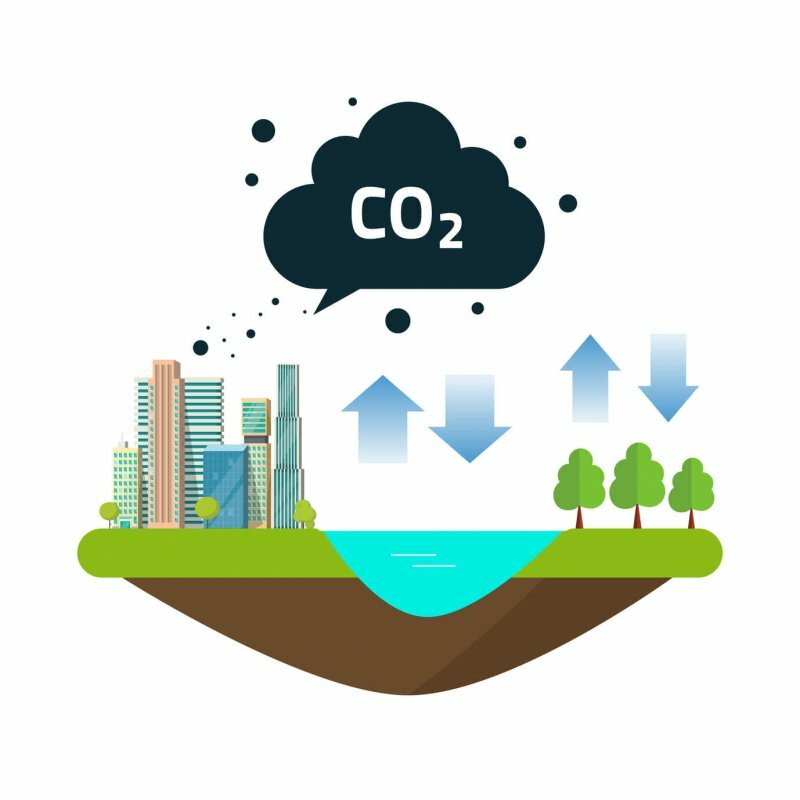
The carbon cycle
Plants and animals breathe, and doing so releases carbon dioxide. In this way, carbon dioxide goes into the atmosphere and plants take it back up through photosynthesis. In this way, the inorganic carbon dioxide molecule becomes an organic compound.
The carbon cycle began millions of years ago by volcanic emissions that released carbon dioxide to the Earth's surface. The original atmosphere of the planet was composed mainly of CO2 and most of it was captured by the oceans, the organisms alive and the ground.
The role regarding the greenhouse effect
As a consequence of the carbon cycle, the greenhouse effect has remained in Balance for millions of years. However, in recent decades this situation has been changing due to the effect of human action.
The atmosphere around us is heated by the effects of the Sun and the heat tends to drift away. Despite this, certain gases in the atmosphere prevent it from escaping and returning some of this heat to the surface. More than 70% of the heat retained by carbon dioxide generates the so-called greenhouse effect.
 If the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere increases, more heat is retained than necessary and, therefore, the levels of temperature increase. This increase in temperature has been produced by the burning of fuels such as oil, coal and gas.
If the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere increases, more heat is retained than necessary and, therefore, the levels of temperature increase. This increase in temperature has been produced by the burning of fuels such as oil, coal and gas.
In other words, industries and production from Energy they are the cause of the generation of the greenhouse effect. The consequences of all this are potentially devastating: rising sea levels, floods or storms.
Photos: Fotolia - vladwel / bluering
Carbon Dioxide Topics

