Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in May. 2010
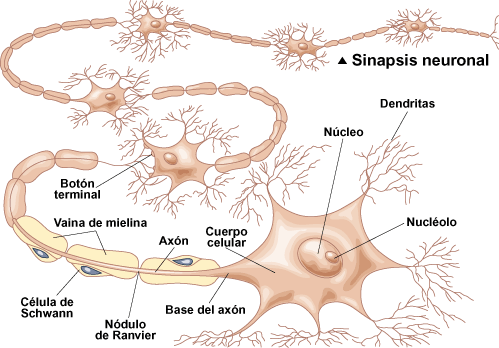 It is designated by the term of synapse to functional contact relationship between nerve cell endings and it is precisely at the instigation of these impulses that the transmission of impulse highly strung. The word derives from a Greek word that refers union or bond, because ultimately it is the specialized intercellular junction between neurons.
It is designated by the term of synapse to functional contact relationship between nerve cell endings and it is precisely at the instigation of these impulses that the transmission of impulse highly strung. The word derives from a Greek word that refers union or bond, because ultimately it is the specialized intercellular junction between neurons.
The synapse begins with an electrical chemical discharge on the membrane of the cell transmitter or presynaptic, meanwhile, when the aforementioned impulse reaches the end of the axon (long and thin prolongation of the neuron), the neuron secretes a substance that will lodge in the synaptic space between the transmitting neuron and the receiving or postsynaptic neuron.
Furthermore, the aforementioned neurotransmitter will be responsible for exciting another neuron.
Depending on the type of transmission of the nerve impulse, the synapse may be chemical or electrical.
In the electrical synapse, the pre and post synaptic processes turn out to be constant as a consequence of the cytoplasmic union of molecules of
protein tubular, which make it easier for the stimulus move from one cell to another without the need for chemical interventions.Due to this shape, the electrical synapse will provide a low endurance between neurons and a minimal delay in synaptic transmission that does not intervene any chemical mediator.
And for its part, the chemical synapse is the most common synapse of the two. In this type, the neurotransmitter acts as a bridge between the two neurons, it diffuses into the synaptic space, adhering to receptors that happen to be special protein molecules that are located on the post membrane synaptic ..
The union that occurs between neurotransmitters and receptors of the postsynaptic membrane causes modifications in membrane permeability, while the nature of both the neurotransmitter and of the molecule of the receptor will determine if the effect that is produced corresponds to that of excitation or inhibition of the postsynaptic neuron.
Topics in Synapse