VAT Accounting Record: Accounting Aspect
Accounting / / November 13, 2021
As can be seen, from the above, the value added tax is caused by an infinity of values and, in addition, there are different rates; Therefore, to determine it correctly, it is necessary to know several aspects, such as the activity or business of the company, the zone or place of location, the special concessions granted, etc., so that according to them the rate is applied correspondent.
Once the corresponding rate is specified, the value added tax (VAT) is determined by multiplying the value of the alienation, the provision of services, the temporary use or enjoyment of goods or the importation of goods and services by the applicable rate.
Accounts used to record VAT. The accounts that are established to register the VAT that the taxpayer transfers to his clients and that transferred to him or passed on by his suppliers, are the following:
VAT payable. This account is of Current Liabilities, of a creditor nature, in it is registered the 379 YA that the taxpayer transfers, charges or charges his clients.

This account is also called VAT Accrued, Taxes Payable, or Sundry Creditors. 38i

Creditable VAT. This account is a Current Asset account, of a debtor nature, it registers the 382 VAT that is transferred to the taxpayer or passed on by its suppliers.
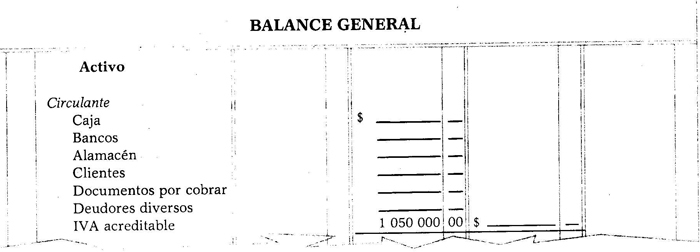
This account is also called VAT to be credited, output VAT, VAT paid, or 384 different debtors.

VAT payable on operations carried out during the month:

Creditable VAT of operations carried out during the month:
Determination of the integer * of the VAT. The entire value of the VAT is determined by subtracting creditable VAT from the VAT payable. Example:
VAT Payable $ 1,350,000.00
Less: VAT creditable 1,050,000.00
Total amount of VAT $ 300,000.00
It should be borne in mind that the taxpayer must pay the entire value added tax monthly, at the latest on the 20th or at the next business day, if it is not, of each of the months of the fiscal year, by means of a statement that he will present at the offices authorized.
In order to better understand the above, the resolution of a practical case is presented below, relating to the main operations carried out by a company whose activity or business is the: or sale of household items, which cause 15% of the VAT.
