Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / November 13, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., in Jun. 2015
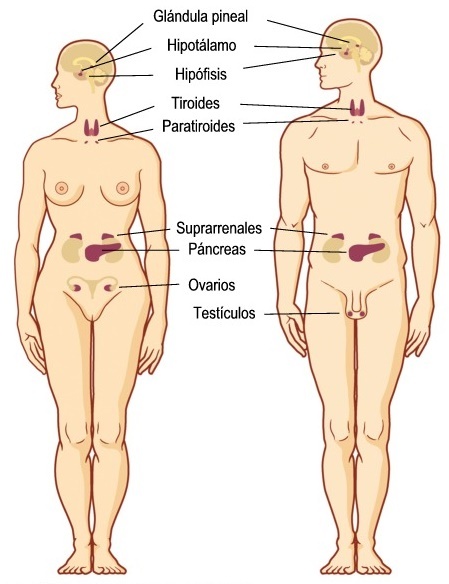 The Glands are structures that have the ability to produce substances that are capable of producing an effect on another organ, these can be released into the blood, into a cavity such as the inside of a viscus or into the surface bodily.
The Glands are structures that have the ability to produce substances that are capable of producing an effect on another organ, these can be released into the blood, into a cavity such as the inside of a viscus or into the surface bodily.
Types of glands
The final destination of the substances that are produced causes the glands to be classified into two large groups:
Endocrine glands. They are those glands that release their secretions into the blood so that they travel through the body, this occurs in the cases of hormones that are produced in a gland and have an effect in a place distant from the Body.
Exocrine glands. In this case, the secretion is released near the site where they are produced, for which the gland has an excretory duct that transports it to the interior of a viscus as occurs with the secretions of the pancreas that are drained through the Wirsung duct towards the intestine, specifically towards the duodenum, the breasts that secrete milk or the sweat glands that release sweat towards the skin.
Endocrine glands
The endocrine glands are part of the endocrine system, a system that is responsible for the control of organs related to important functions such as the metabolism, regulation of blood pressure, sexual activity and reproduction. It is made up of several glands.
Pineal. This gland is located inside the skull at the level of the brain, where Melatonin is produced, a hormone responsible for regulating the sleep-wake cycle.
Hypothalamus It is a structure of the nervous system found in the brain and has the function of regulating the other glands of the endocrine system through the production of releasing agents that are necessary for the hormonal secretion of the pituitary gland to be activated.
Hypophysis. It is a structure that is also located in the skull and is contained in a bone structure known as the sella turcica. She releases the stimulating agents from the other glands.
Thyroid. It is a structure that is located in the neck, where the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 are produced by the action of TSH produced in the pituitary, these hormones are necessary to activate the different processes related to the metabolism.
Parathyroid. There are four small glands that are located behind the thyroid, they produce parathormone, substance necessary to regulate calcium metabolism and maintain stable levels in the blood.
Adrenals There are two glands located one on each kidney, there are produced several hormones such as aldosterone related to the control of blood pressure, cortisol, and male-type sex hormones or androgens (in both men and women) woman).
Pancreas. The pancreas is an endocrine and exocrine gland. Its endocrine activity is based on the production of the main hormone insulin related to the metabolism of carbohydrates and the maintenance From blood sugar levels within normal limits, the insulin-regulating hormone glucagon is also produced there. From the exocrine point of view, the pancreas produces amylases, lipases and proteases, enzymes that are released into the digestive tract for the digestion of food.
Ovaries They are two structures located on the sides of the uterus that have the function of producing estrogens, The main female sex hormone required to stimulate sexual activity, ovulation, and reproduction.
Testicles They are two structures located in the scrotum that produce testosterone, the main male sex hormone necessary for sexual activity and the production of sperm.
 There are other structures capable of releasing hormones into the bloodstream without being glands, such is the case of the kidneys, which produce erythropoietin, substance needed to stimulate the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow and adipose tissue that produces a hormone related to appetite called leptin.
There are other structures capable of releasing hormones into the bloodstream without being glands, such is the case of the kidneys, which produce erythropoietin, substance needed to stimulate the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow and adipose tissue that produces a hormone related to appetite called leptin.