Definition of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Equilibrium
Miscellanea / / December 12, 2021
Conceptual definition
The equilibrium of a chemical reaction can be homogeneous, if all the reactants and products are in the same state of aggregation or heterogeneous if different products and reactants are involved phases.

Chemical engineer
Homogeneous Equilibria
In general, acid-base equilibria are homogeneous, since they occur in aqueous solutions. Likewise, the degree of ionization of each acid or base will give rise to the pH of the solution and this process is governed by the acidity or basicity constant, known as Ka and Kb respectively.
Here is an example of Balance homogeneous chemical and its respective equilibrium constant:
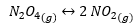
Being:
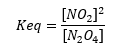
It should be remembered that chemical equilibrium occurs when the reaction speed direct equals speed indirect reaction.
Heterogeneous Equilibria
In general, we attribute them to solutions or precipitations of ionic compounds since their initial or final phase responds to a solid that is diluted or precipitated in aqueous solution. It should be noted that, in these cases, the constant that governs the process is the equilibrium constant Keq, however, the solids do not come into play in the products of this constant.
A clear example of a heterogeneous equilibrium is the decomposition at high temperature of solid calcium carbonate forming solid calcium oxide and gaseous carbon dioxide:
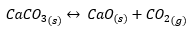
Being:
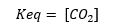
Heterogeneous solid-liquid equilibria
In heterogeneous equilibria where a solid precipitates, the solubility product constant or Kps plays a fundamental role, and is it, in this case, the equilibrium constant that governs the process, indicating how soluble the solid is in the solvent used, commonly Water.
What is this about? Practically, to the formation of an insoluble or slightly soluble product from an ionic compound, therefore, in these cases there are a series of factors They play an important role.
In the first place, as in all equilibrium, the temperature, since the increase in temperature leads to an increase in the Kinetic energy of the crystals that weakens the bonding forces due to the vibrations caused.
On the other hand, the nature of the interacting compounds, since, as we know, the greater the similarity in polarity of the solvent and the compound to be dissolved, the better the degree of solubility. This is explained since the magnitude of the interacting forces between the solvent and the solid to be dissolved must be similar to those that the solid initially possessed.
Finally, the entropy of the system plays a very important role. The entropy variation explains the degree of order of a system and, as is known, the Universe always tends towards chaos or disorder. When the dissolution takes place, the bonds of the ionic compound are broken increasing the disorder, therefore, the process is widely favored.
So when an ionic compound dissolves in the direct sense of the equilibrium reaction and, precipitates, in the opposite sense, the relation that governs the process is the constant of the solubility product mentioned.
In both types of equilibria we can highlight common characteristics: first, temperature plays a fundamental role, since it controls the equilibrium. If this variable varies, by Le Chatelier's Principle the system will react in such a way as to counteract said disturbance. Likewise, the value of the equilibrium constant is unique for each equilibrium reaction at a given temperature and corresponds to a quotient of activities, so it is independent of the concentration or pressure of products and reagents. To deepen the study of the variation of Keq with temperature, it is necessary to delve into the Equation by Van’t Hoff.
Second, the state of equilibrium must not vary over time and when we speak of a state of equilibrium we refer to a process that takes place in a closed system.
On the other hand, in all cases, the expression of the equilibrium constants, whatever the process carried out, retains its shape being: concentration of products raised to their respective stoichiometric coefficients with respect to reagent concentration raised to their coefficients stoichiometric. It should be noted that most of these constants have been tabulated at 25ºC.
Bibliography
Chair notes, General Chemistry I, UNMdP, Faculty of Engineering, 2019.
Topics in Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Equilibrium

