Difference between Formal Sciences and Factual Sciences
Miscellanea / / February 26, 2022
The main difference between formal sciences and factual sciences lies in its object of study. The formal sciences they study and describe abstract entities, that is, entities that have no correlation in nature. Instead, the factual sciences they observe and analyze objective facts, that is, events or objects that exist in the real world.
For example: Mathematics is a formal science because it studies the relationships and properties of numbers, which are abstract entities. Instead, astronomy is a factual science because it analyzes the behavior and properties of celestial bodies, which are concrete entities.
These two sciences also differ in the methodology they employ, and in the statements, symbols, and results they produce.
However, they present similarities, for example, both elaborate theories or concepts that must be verified using a rigorous methodology and that can be superseded or refuted in the future.
In addition, both the formal sciences and the factual sciences aim to increase and improve knowledge and the criteria to develop it.
| formal sciences | factual sciences |
| They study abstract entities and their relationships. | They study concrete entities and their relationships. |
| They use the deductive method. | They use the scientific method. |
| They produce statements that describe relations between ideal signs. | They produce sentences that describe relations between signs that represent elements or facts of the real world. |
| They use rational and interpretable symbols. | They use certain symbols. |
| They arrive at logical results. | They arrive at empirically verifiable results. |
| For example: mathematics, logic, geometry. | For example: history, economics, psychology. |
Characteristics of the formal sciences
Characteristics of factual sciences
Types of factual sciences
There are two types of factual sciences:
Examples of formal sciences
- Math. It is the study of the properties and relationships of calculations, numbers, and other symbols.
- Logic. It is the study of the propositions and reasoning of thought.
- Computer's science. It is the study of the properties and operation of computer systems.
- Arithmetic. It is the study of numbers and the operations that can be performed with them.
- Statistics. It is the study, analysis and production of data, probabilities and proportions.
- Geometry. It is the study of the properties and relationships of geometric shapes.
- Algebra. It is the study of abstract mathematical structures and their combinations.
- Trigonometry. It is the study of the characteristics and relationships of triangles.
Examples of factual sciences
- Physical. It is the study of the laws that explain the functioning of the universe.
- Chemistry. It is the study of the origin, composition and transformation of matter.
- biology. It is the study of the characteristics and behavior of living things.
- Sociology. It is the study of societies, the relationships of their individuals and the events that occur in them.
- Economy. It is the study of the production and trade of goods and services at a regional, national or global level.
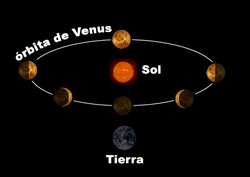
- Astronomy. It is the study of bodies and the phenomena of space and the universe.
- geology. It is the study of the compositional and structural characteristics of the outer and inner parts of the Earth. In addition, its formation and history are studied.
- History. It is the study of facts, processes and civilizations of human beings that took place in the past.
- Psychology. It is the study of the characteristics, structure, formation and functioning of the human mind.
- Botany. It is the study of the structure, characteristics and classification of plants.
- political science. It is the study of the structure, formation, operation and changes of the forms of government and social organizations.
- Paleontology. It is the study of living beings that inhabited the Earth in the past. To do this, the fossil remains of these beings are analyzed.
It can serve you: