Distillation Tower/Column Definition
Reliability Electric Resistance / / April 02, 2023

Chemical engineer
Distillation towers or columns are pressure vessels where the separation of the various components that make up the feed stream occurs. The operating principle is based on the difference between the evaporation temperatures of each of the substances and their volatility.
Theoretical fundament
Like all distillation, the essence of the process is based on the scheme:
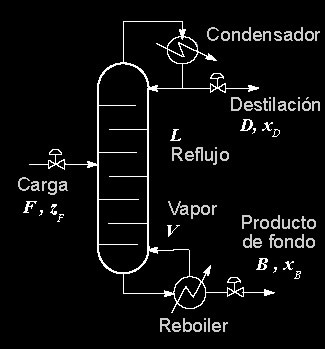
A distillation tower has a heat source in the lower area, such as the Reboiler, which generates that, thanks to the delivery of caloric energy, part of the components (one or more) pass into the vapor phase. As they ascend through the column, they will encounter the descending liquid, for Therefore, when it reaches the top of the column, the steam current is fed by the most volatile Meanwhile, the heavier components were dragged by the liquid that descended in a countercurrent flow. This is why liquid streams are said to be at their bubble point, while vapor streams are said to be at their dew point.
When these currents exchange energy, they simultaneously exchange mass and that happens at each stage, that is, on each plate (it could also be a filling) symbolized as an inner horizontal line in the tower.
When the vapor fraction reaches the top of the tower, it goes to a condenser, where it is obtained the distilled product and where a portion of that stream, known as reflux, re-enters the tower.
It must be taken into account that in the previous image a binary type distillation is graphed, that is, only two components in the power current They are separated, extracting one from the top and the other from the bottom. However, there are distillations of multiple components, where in each stage of the tower it is possible to separate a different component.
Applications
The industries that use distillation towers are many and, therefore, depending on their use will be the diameter and length, the manufacturing material and its type of plate or filling. For example, a distillation tower is the refineries heart of crude oil in the world. When the oil arrives at a treatment plant, it first undergoes a desalination process and then high-pressure furnaces. temperature. Then, it is introduced to the tower itself, where the more volatile components rise through the stages and the of higher boiling temperature fall towards the bottom of the tower and the condensates at the top are collected in buckets.
To maintain the temperature of the tower there are various mechanisms, particularly here diesel oil is usually recycled and kerosene (components of the original mixture), prior to their re-entry, they are cooled in a heat exchanger. heat. Whereas, at the top, the “reflux head” maintains the right temperature at the top.
To understand the significant size of these towers, between 60 m and 80 m in length and 6 m in diameter, we must understand the importance of this in the process. From the initial mixture, it is possible to separate heavy diesel oil (at 340 °C), light diesel oil (at 280 °C), kerosene (at 210 °C) and naphtha (at 180 °C), from there derives the extensive length necessary to cover all the fractionation stages of the mix. In turn, the heaviest component is obtained at the bottom of the tower: fuel oil.
In fractionation plants they are also used to sweeten the gas, for example, in amine contactor towers, it is obtained from the top the sweet gas, while at the bottom the amine current with acid gas content, current that is sent to another tower for its regeneration. They are also used in other industries, such as in the production of organic compounds and of polymers.
As expected, there is also a variety of manufacturing materials, from glass for distillation columns to scale laboratory or pilot scale to large towers made of carbon steel or low alloy steel. On the other hand, if it is known that they will work with a highly corrosive fluid such as gases with CO2 and H2S content, they are usually made of stainless steel or other resistant alloys. It is also common to find towers with different materials depending on the sections, since, for example, the critical zone of condensation For acid gases, the upper section can be made of stainless steel or have a cladding while the lower section can be made of carbon steel.
Its design is done based on your service and must meet rigorous standards of quality, security and manufacturing that provide design standards, such as ASME VIII.



