Respiratory System Example
Biology / / July 04, 2021
The respiratory system It is the mechanism that all living beings have to synthesize their food (sugars and carbohydrates among others).
These respiratory systems can be divided into:
- Lung breathing
- Branchial breathing
- Skin respiration
- Tracheal breathing
- Direct broadcast
- Photosynthesis
These respiratory systems are developed according to the requirements of each type of living being and in plants its requirement of carbon dioxide that it needs, expelling oxygen.
So, taking into account that every living being has a breathing system, we must explain the difference and how each one works.
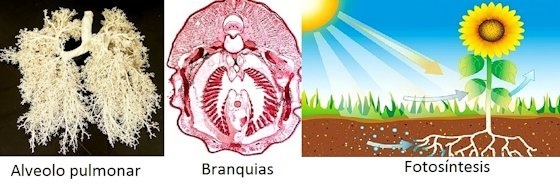
Example of respiratory system:
1.- Lung respiration.- This system obeys the respiration that takes place in two large bags that are filled with capillaries (veins and arteries where carries out circulatory respiration), thus, the oxygen that circulates throughout the body is introduced directly into the cells, subsequently expelling carbon dioxide into the blood, which is transported through the veins to the lungs, where the material of waste.
The mechanism begins with the respiratory tract (nose and mouth), where the air enters, moistens and warms up in the nostrils, passing later through the pharynx, larynx, trachea, throat and bronchi, finally reaching the capillary area (lung tissue), and here, being in the alveoli, gas changes are carried out, supporting the gas exchange by the pressure of the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm.
This respiration occurs in complex living beings, such as large ones, birds, aquatic mammals, carnivores and primates, among others.
2.- branchial respiration.- This breathing system corresponds to higher or complex animals, but found in the aquatic world; fish, some reptiles in the larval stage and insects in the larval stage are found here. All of these have a high oxygen requirement.
The process is carried out by absorbing large amounts of water that pass through the gills, which are organs filled with blood vessels where gas exchange takes place.
These organs are usually superficial, especially in the insects and larvae already mentioned, and deep in the rest.
3.- Skin respiration.- This type of respiration exists in simple living beings such as worms, earthworms and some amphibians such as toads and frogs, that even with lungs, being in the water breathe through the skin.
In this respiration, the surface of the skin performs the function of absorbing oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide, as is done in the lungs but on a small scale.
4.-Tracheal breathing.- This respiration consists of small tubes (tracheae), it is found in insects and arthropods such as spiders and even scorpions, where gas changes are made, in these small tubes circulates the air necessary for the life of the insect. The function of the trachea is similar to that of cutaneous respiration but with greater efficiency and a greater amount of oxygen.
5.- Direct broadcast.- This occurs in animals or simpler living beings, which require a tiny amount of oxygen, so that their respiration takes place directly on the cell membrane.
In this system are:
- Protozoa
- Sponges
- Corals etc.
6.- Photosynthesis.- The respiration of plants is inverse to that of the rest of living beings, they use carbon dioxide and expel oxygen, and for this they require carbon dioxide, For this they use the effects of the sun that when in contact with the leaves, react with the chlorophyll that produces glucose releasing oxygen to the environment as a product of waste.
It can be considered as the respiration of plants, regardless of being opposed to the general concept of respiration.
