Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in Dec. 2014
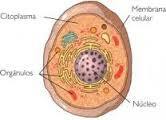 Cytoplasm is one of the parts, basic elements of the cell, which is located between the plasma membrane and the nucleus, in eukaryotic cells, and in cells prokaryotes that, since they do not have a nucleus, use the cytoplasm to house their material genetic.
Cytoplasm is one of the parts, basic elements of the cell, which is located between the plasma membrane and the nucleus, in eukaryotic cells, and in cells prokaryotes that, since they do not have a nucleus, use the cytoplasm to house their material genetic.
Basically, the cytoplasm is in charge of developing all the chemical reactions of living beings and is eminently made up of water and also by ionized mineral substances and organic substances such as enzymes Y protein.
Its relevant functions are three: nutrition, since in it those substances are incorporated that will be later transformed to release Energy; storage, deals with storing certain substances that will be used in the future and it is important that they are there while waiting for your need to use them; and the structural, since the cytoplasm is that part that gives the cell its shape and that will be the starting point of all its movements.
If it is observed in detail through the microscope it will be appreciated that one of its characteristic features is the
appearance grainy that it boasts and that is due to the large number of organelles (cell organs), ribosomes, among others, that its conformation presents. Ribosomes perform the essential function of synthesizing proteins.Without a doubt the microscope was key in advancing the knowledge of the cytoplasm. The detailed and precise physical study that this apparatus allowed implied to bring to light much knowledge about the cytoplasm, the one indicated above the presentation grainy, and on the other hand also allowed decide its viscosity and the identification of the cytoskeleton, which are hair-like structures within the cytoplasm and which can be found in many types of cells.
Topics in Cytoplasm
