Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in Jan. 2010
 Ribosomes are each of the organelles of living cells, composed of ribonucleic acid and protein and that deal with the synthesis of the latter.
Ribosomes are each of the organelles of living cells, composed of ribonucleic acid and protein and that deal with the synthesis of the latter.
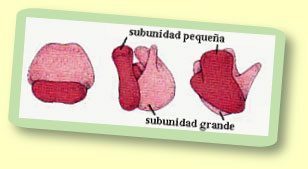
As a consequence of their small size, 28 nm in the case of prokaryotic cells and 32 nm in that of eukaryotes, the ribosomes, only, are perceptible through a microscope electronic, and recognizable by its roundness. These organelles consist of two parts, a major and a minor subunit, both leaving the nucleus mobile but separately and that will be held together through charges. We can find ribosomes in any type of cell except one, sperm.
As we mentioned above, ribosomes are attributed a super fundamental function which is to be the organelles that are responsible for the synthesis of proteins through a process known as translation. On the other hand, translation turns out to be the second step of protein synthesis, it occurs in the cytoplasm where the ribosomes are found. So in this complex process a RNA messenger, which is the ribonucleic acid that contains the information
genetics that comes from DNA and that is used at the behest of protein synthesis and that will end up determining the order in which the amino acids, it is deciphered and produces a specific polypeptide that will be in clear harmony with the rules established by the code genetics in question, while and at the same time, translation is made up of four phases: activation, initiation, elongation and termination.All proteins are made up of amino acids, what's more, so far scientific research that have been carried out in this regard, indicate that at least 20 amino acids have been detected in human beings alive.
Topics in Ribosomes